案例測試:
1. Master新增網卡,修改server端配置
IP : 192.168.40.128/24
註釋: bind,支持網絡連接
2. 新建虛機slave,配置網絡,修改redis配置
#slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
slaveof 192.168.40.128 6379
# masterauth <master-password>
masterauth "zcy1991"
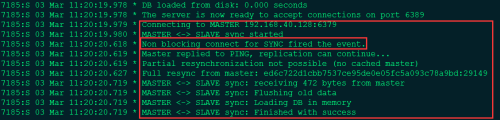
3. 啓動redis,打開日誌
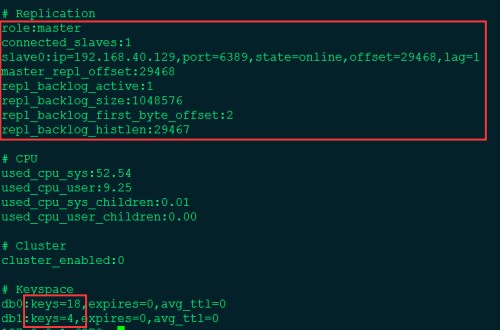
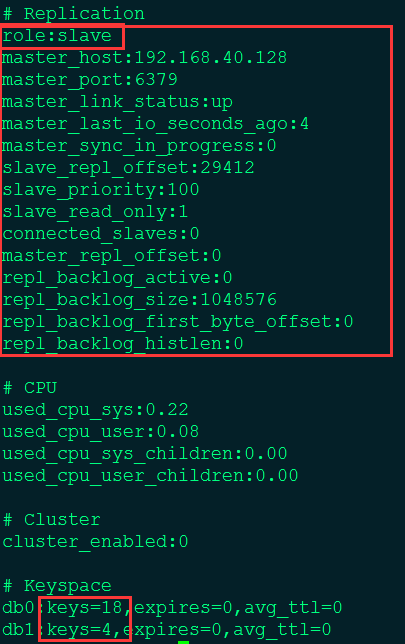
4. 查看Replication信息
Master:
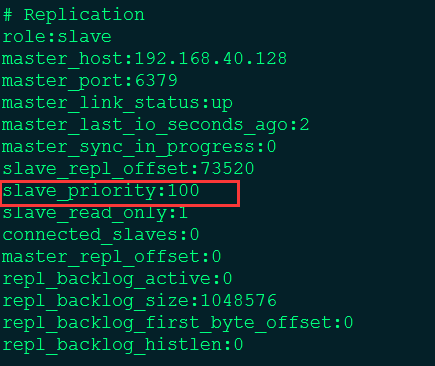
Slave:
5.配置文件 “主從複製”部分 【翻譯+理解】 (Verion 3.2.8)
################################# REPLICATION (複製) #################################
-------------------------------------------
# Master-Slave replication. Use slaveof to make a Redis instance a copy of
# another Redis server. A few things to understand ASAP about Redis replication.
#主從複製。 使用slaveof使一個Redis實例成爲另一個Redis服務器的拷貝(副本)。
關於Redis複製的幾個事情:
# 1) Redis replication is asynchronous, but you can configure a master to
# stop accepting writes if it appears to be not connected with at least
# a given number of slaves.
1) Redis複製是異步的,但是如果它看起來沒有與至少給定數量的slave連接,您可以配置一個主設備停止接受寫入。
# 2) Redis slaves are able to perform a partial resynchronization with the
# master if the replication link is lost for a relatively small amount of
# time. You may want to configure the replication backlog size (see the next
# sections of this file) with a sensible value depending on your needs.
2) 如果複製鏈路丟失相對較少的時間,Redis slave能夠與master執行部分重新同步。 您可能需要根據需要,使用合理的值配置replication backlog 大小(請參閱此文件的下一個操作)。
# 3) Replication is automatic and does not need user intervention. After a
# network partition slaves automatically try to reconnect to masters
# and resynchronize with them.
# 3) 複製是自動的,不需要用戶干預。 網絡分割後,slaves 自動嘗試重新連接到masters 並與它們重新同步。
# slaveof <masterip> <masterport>
# If the master is password protected (using the "requirepass" configuration
# directive below) it is possible to tell the slave to authenticate before
# starting the replication synchronization process, otherwise the master will
# refuse the slave request.
#如果master使用密碼保護(使用下面的“requirepass”配置指令),可以在開始複製同步過程之前,告訴slaves進行認證,否則master將拒絕slave連接請求。
# masterauth <master-password>
-------------------------------------------
# When a slave loses its connection with the master, or when the replication
# is still in progress, the slave can act in two different ways:
#當一個slave與master斷開連接或複製仍在進行時,slave可以採用兩種不同的方式:
# 1) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'yes' (the default) the slave will
# still reply to client requests, possibly with out of date data, or the
# data set may just be empty if this is the first synchronization.
# 如果slave-serve-stale-data設置爲“yes”(默認值),則slave仍將回復客戶端請求,可能使用過期數據,或者如果這是第一次同步,則數據集可能爲空。
# 2) if slave-serve-stale-data is set to 'no' the slave will reply with
# an error "SYNC with master in progress" to all the kind of commands
# but to INFO and SLAVEOF.
#如果slave-serve-stale-data設置爲“no”,除了INFO和SLAVEOF,slave將回復錯誤“SYNC with master in progress”給所有類型的命令。
slave-serve-stale-data yes
# You can configure a slave instance to accept writes or not. Writing against
# a slave instance may be useful to store some ephemeral data (because data
# written on a slave will be easily deleted after resync with the master) but
# may also cause problems if clients are writing to it because of a
# misconfiguration.
# 您可以配置slave實例接受寫入或不接受寫入。 對slave實例進行寫操作對存儲一些臨時數據可能是有用的(因爲寫在slave上的數據將在與master重新同步後很容易被刪除),但是如果客戶端因爲錯誤配置而寫入它,也會導致問題。
#
# Since Redis 2.6 by default slaves are read-only. 自2.6之後,slaves默認只讀(不可寫)
#
# Note: read only slaves are not designed to be exposed to untrusted clients
# on the internet. It's just a protection layer against misuse of the instance.
# Still a read only slave exports by default all the administrative commands
# such as CONFIG, DEBUG, and so forth. To a limited extent you can improve
# security of read only slaves using 'rename-command' to shadow all the
# administrative / dangerous commands.
# 注意:只讀slaves並不設計爲了暴露給互聯網上的不受信任的客戶端。 它只是一個防止濫用實例的保護層。 Slaves默認情況下仍然可以導出所有管理命令,如CONFIG,DEBUG等。 在有限的程度上,您可以使用“rename-command”來提高只讀從設備的安全性,以隱藏所有管理/危險命令。
#作爲從服務器,默認情況下是隻讀的(yes),可以修改成NO,用於寫(不建議
slave-read-only yes
-------------------------------------------
# Replication SYNC strategy: disk or socket. 複製同步策略: disk或socket
#
# -------------------------------------------------------
# WARNING: DISKLESS REPLICATION IS EXPERIMENTAL CURRENTLY 警告:無磁盤的複製當前還處於試驗階段。
# -------------------------------------------------------
#
# New slaves and reconnecting slaves that are not able to continue the replication
# process just receiving differences, need to do what is called a "full
# synchronization". An RDB file is transmitted from the master to the slaves.
# The transmission can happen in two different ways:
#是否使用socket方式複製數據。目前redis複製提供兩種方式,disk和socket。如果新的slave連上來或者重連的slave無法部分同步,就會執行全量同步,master會生成rdb文件。有2種方式:disk方式是master創建一個新的進程把rdb文件保存到磁盤,再把磁盤上的rdb文件傳遞給slave。socket是master創建一個新的進程,直接把rdb文件以socket的方式發給slave。disk方式的時候,當一個rdb保存的過程中,多個slave都能共享這個rdb文件。socket的方式就的一個個slave順序複製。在磁盤速度緩慢,網速快的情況下推薦用socket方式。
#新的slaves和重新連接的slaves,不能繼續複製過程只是接收差異,需要做的就是所謂的“完全同步”。 一個RDB文件從master傳輸到slaves。
# 傳輸可以以兩種不同的方式發生:
# 1) Disk-backed: The Redis master creates a new process that writes the RDB
# file on disk. Later the file is transferred by the parent
# process to the slaves incrementally.
磁盤支持:Redis master創建一個新進程,負責將RDB文件寫入磁盤。 稍後,該文件由父進程以增量方式傳送到slaves。
# 2) Diskless: The Redis master creates a new process that directly writes the
# RDB file to slave sockets, without touching the disk at all.
#無盤:Redis master創建一個新的進程,直接將RDB文件寫入slaves sockets,而不觸及磁盤。
# With disk-backed replication, while the RDB file is generated, more slaves
# can be queued and served with the RDB file as soon as the current child producing
# the RDB file finishes its work. With diskless replication instead once
# the transfer starts, new slaves arriving will be queued and a new transfer
# will start when the current one terminates.
#使用"磁盤支持"的複製,在生成RDB文件時,只要生成RDB文件,當前子進程就完成了它的工作,更多的slaves就可以排隊並被提供這一份RDB文件。(可同時提供給多個slaves)
# 使用無盤複製,一旦傳輸開始,新slaves到達將排隊,並且噹噹前的一個終止時,新的傳輸將開始。(順序複製,一個接一個)
# When diskless replication is used, the master waits a configurable amount of
# time (in seconds) before starting the transfer in the hope that multiple slaves
# will arrive and the transfer can be parallelized.
#當使用“無盤複製”時,master在開始傳輸之前等待可配置的時間量(以秒爲單位),希望多個slaves將到達並且傳輸可以並行化。
#
# With slow disks and fast (large bandwidth) networks, diskless replication
# works better. 使用慢磁盤和快速(大帶寬)網絡,無盤複製工作更好(建議socket)
repl-diskless-sync no
# When diskless replication is enabled, it is possible to configure the delay
# the server waits in order to spawn the child that transfers the RDB via socket
# to the slaves.
diskless複製的延遲時間,防止設置爲0。一旦複製開始,節點不會再接收新slave的複製請求直到下一個rdb傳輸。所以最好等待一段時間,等更多的slave連上來。
#當啓用無磁盤複製時,可以配置服務器等待的延遲,以便產生子進程,通過socket傳輸RDB給slaves。
# This is important since once the transfer starts, it is not possible to serve
# new slaves arriving, that will be queued for the next RDB transfer, so the server
# waits a delay in order to let more slaves arrive.
#這是很重要的,因爲一旦傳輸開始,不可能服務新到達的slaves,它們將爲下一個RDB傳輸排隊,所以服務器等待一段時間,以便讓更多的slaves到達。
-------------------------------------
# The delay is specified in seconds, and by default is 5 seconds. To disable
# it entirely just set it to 0 seconds and the transfer will start ASAP.
# 延遲以秒爲單位指定,默認值爲5秒。要完全禁用它,僅僅設置爲0秒即可,傳輸將盡快開始。
repl-diskless-sync-delay 5
# Slaves send PINGs to server in a predefined interval. It's possible to change
# this interval with the repl_ping_slave_period option. The default value is 10
# seconds.
#slaves以預定義的時間間隔向服務器發送PING。可以使用repl_ping_slave_period選項更改此時間間隔。默認值爲10秒。
#
# repl-ping-slave-period 10
-------------------------------------------
複製連接超時時間。master和slave都有超時時間的設置。master檢測到slave上次發送的時間超過repl-timeout,即認爲slave離線,清除該slave信息。slave檢測到上次和master交互的時間超過repl-timeout,則認爲master離線。需要注意的是repl-timeout需要設置一個比repl-ping-slave-period更大的值,不然會經常檢測到超時。
# The following option sets the replication timeout for: 設置複製timeout
#
# 1) Bulk transfer I/O during SYNC, from the point of view of slave. 從slave角度看,批量傳輸I / O在SYNC期間。
# 2) Master timeout from the point of view of slaves (data, pings). 從slave角度看,master 超時(data,pings)
# 3) Slave timeout from the point of view of masters (REPLCONF ACK pings). 從masters角度看,slave超時(REPLCONF ACK pings)
#
# It is important to make sure that this value is greater than the value
# specified for repl-ping-slave-period otherwise a timeout will be detected
# every time there is low traffic between the master and the slave.
#重要的是確保此值大於爲repl-ping-slave-period指定的值,否則每次master和slave之間的流量低時都會檢測到超時。
#
# repl-timeout 60
-------------------------------------------
是否禁止複製tcp鏈接的tcp nodelay參數,可傳遞yes或者no。默認是no,即使用tcp nodelay。如果master設置了yes來禁止tcp nodelay設置,在把數據複製給slave的時候,會減少包的數量和更小的網絡帶寬。但是這也可能帶來數據的延遲。默認我們推薦更小的延遲,但是在數據量傳輸很大的場景下,建議選擇yes。
# Disable TCP_NODELAY on the slave socket after SYNC? SYNC之後在slave socket上禁用TCP_NODELAY?
#
# If you select "yes" Redis will use a smaller number of TCP packets and
# less bandwidth to send data to slaves. But this can add a delay for
# the data to appear on the slave side, up to 40 milliseconds with
# Linux kernels using a default configuration.
#如果選擇“是”,Redis將使用較少數量的TCP數據包和較少帶寬將數據發送到從站。但是這可能會增加數據出現在對端slave上的延遲,對於Linux內核,使用默認配置可以延遲40毫秒。
# If you select "no" the delay for data to appear on the slave side will
# be reduced but more bandwidth will be used for replication.
#如果選擇“否”,數據在slave端出現的延遲將減少,但更多的帶寬將用於複製
# By default we optimize for low latency, but in very high traffic conditions
# or when the master and slaves are many hops away, turning this to "yes" may
# be a good idea.
#默認情況下,我們針對低延遲進行優化,但在非常高的流量情況下,或者當master和slave相隔許多跳時,將其轉換爲“yes”可能是個好主意。
repl-disable-tcp-nodelay no
---------------------------------------
複製緩衝區大小,這是一個環形複製緩衝區,用來保存最新複製的命令。這樣在slave離線的時候,不需要完全複製master的數據,如果可以執行部分同步,只需要把緩衝區的部分數據複製給slave,就能恢復正常複製狀態。緩衝區的大小越大,slave離線的時間可以更長,複製緩衝區只有在有slave連接的時候才分配內存。沒有slave的一段時間,內存會被釋放出來,默認1m。
# Set the replication backlog size. The backlog is a buffer that accumulates
# slave data when slaves are disconnected for some time, so that when a slave
# wants to reconnect again, often a full resync is not needed, but a partial
# resync is enough, just passing the portion of data the slave missed while
# disconnected.
#設置複製backlog大小。backlog是一個緩衝器(buffer),當slave斷開一段時間時積累slave數據,以便當slave想要再次重新連接時,通常不需要再“完全同步(full resync)”,而是“部分再同步(partial resync)”就足夠了,僅僅傳輸slave在斷開連接時錯失的那部分數據(餘下的)即可。
#
# The bigger the replication backlog, the longer the time the slave can be
# disconnected and later be able to perform a partial resynchronization.
#複製backlog越大,slave可以斷開連接的時間就越長,之後就可以執行”部分重新同步(partial resynchronization)“。
# The backlog is only allocated once there is at least a slave connected. 只有在至少有一個slave連接時才分配backlog。
#
# repl-backlog-size 1mb
# After a master has no longer connected slaves for some time, the backlog
# will be freed. The following option configures the amount of seconds that
# need to elapse, starting from the time the last slave disconnected, for
# the backlog buffer to be freed.
# master沒有slave一段時間會釋放複製緩衝區的內存,repl-backlog-ttl用來設置該時間長度。單位爲秒。
#在master已經不再連接slave一段時間後,backlog將被釋放。 以下選項配置需要經過的秒數,從最後一個slave服務器斷開的時間開始,backlog緩衝區被釋放。
# A value of 0 means to never release the backlog. 值爲0表示永不釋放backlog
#
# repl-backlog-ttl 3600
---------------------------------
# 當master不可用,Sentinel會根據slave的優先級選舉一個master。最低的優先級的slave,當選master。而配置成0,永遠不會被選舉。
# The slave priority is an integer number published by Redis in the INFO output.
# It is used by Redis Sentinel in order to select a slave to promote into a
# master if the master is no longer working correctly.
#slave優先級是由Redis在INFO輸出中發佈的整數。 它由Redis Sentinel使用,以便選擇slave,如果master不再正常工作,則升級爲主設備。
# A slave with a low priority number is considered better for promotion, so
# for instance if there are three slaves with priority 10, 100, 25 Sentinel will
# pick the one with priority 10, that is the lowest.
#具有低優先級編號的slave被認爲更好地用於提升,因此例如如果存在具有優先級10,100,25的三個從設備,則哨兵將選擇具有優先級10,即最低的那個。
# However a special priority of 0 marks the slave as not able to perform the
# role of master, so a slave with priority of 0 will never be selected by
# Redis Sentinel for promotion.
#然而,0的特殊優先級標誌着slave不能執行主設備的角色,因此優先級爲0的從設備將不會被Redis Sentinel選擇用於升級。
# By default the priority is 100.
slave-priority 100
-----------------------------------------
#
# It is possible for a master to stop accepting writes if there are less than
# N slaves connected, having a lag less or equal than M seconds.
#如果連接少於N個slave,具有小於或等於M秒的滯後,則master可以停止接受寫入。
# The N slaves need to be in "online" state.
#
# The lag in seconds, that must be <= the specified value, is calculated from
# the last ping received from the slave, that is usually sent every second.
#以秒爲單位的滯後,必須小於指定值,根據從slave接收的最後一次ping計算,通常每秒發送一次。
# This option does not GUARANTEE that N replicas will accept the write, but
# will limit the window of exposure for lost writes in case not enough slaves
# are available, to the specified number of seconds.
#此選項不保證N個副本將接受寫入,但會在沒有足夠的slave可用的情況下,將丟失寫入的曝光窗口限制爲指定的秒數。
# For example to require at least 3 slaves with a lag <= 10 seconds use: 例如,至少需要3個slave,lag小於10s
#
#redis提供了可以讓master停止寫入的方式,如果配置了min-slaves-to-write,健康的slave的個數小於N,mater就禁止寫入。master最少得有多少個健康的slave存活才能執行寫命令。這個配置雖然不能保證N個slave都一定能接收到master的寫操作,但是能避免沒有足夠健康的slave的時候,master不能寫入來避免數據丟失。設置爲0是關閉該功能。
# min-slaves-to-write 3
# 延遲小於min-slaves-max-lag秒的slave才認爲是健康的slave
# min-slaves-max-lag 10
#設置1或另一個設置爲0禁用這個特性。
# Setting one or the other to 0 disables the feature.
#
# By default min-slaves-to-write is set to 0 (feature disabled) and
# min-slaves-max-lag is set to 10. 默認配置
# A Redis master is able to list the address and port of the attached
# slaves in different ways. For example the "INFO replication" section
# offers this information, which is used, among other tools, by
# Redis Sentinel in order to discover slave instances.
# Another place where this info is available is in the output of the
# "ROLE" command of a masteer.
# Redis master能夠以不同的方式列出所連接slave的地址和端口。 例如,“INFO replication”部分提供此信息,除了其他工具之外,Redis Sentinel還使用該信息來發現slave實例。 此信息可用的另一個地方在masterser的“ROLE”命令的輸出中。
#
# The listed IP and address normally reported by a slave is obtained
# in the following way:
#通常由slave報告的列出的IP和地址,通過以下方式獲得:
# IP: The address is auto detected by checking the peer address
# of the socket used by the slave to connect with the master.
#IP:通過檢查slave與master連接使用的套接字的對等體地址自動檢測地址。
# Port: The port is communicated by the slave during the replication
# handshake, and is normally the port that the slave is using to
# list for connections.
#端口:端口在複製握手期間由slavet通信,並且通常是slave正在使用列出連接的端口。
# However when port forwarding or Network Address Translation (NAT) is
# used, the slave may be actually reachable via different IP and port
# pairs. The following two options can be used by a slave in order to
# report to its master a specific set of IP and port, so that both INFO
# and ROLE will report those values.
#然而,當使用端口轉發或網絡地址轉換(NAT)時,slave實際上可以通過(不同的IP和端口對)來到達。 slave可以使用以下兩個選項,以便向master報告一組特定的IP和端口,以便INFO和ROLE將報告這些值。
# There is no need to use both the options if you need to override just
# the port or the IP address. 如果你需要僅覆蓋端口或IP地址,則沒必要使用這兩個選項。
#
# slave-announce-ip 5.5.5.5
# slave-announce-port 1234
參考資源: