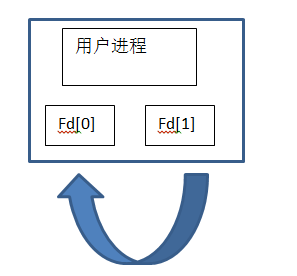
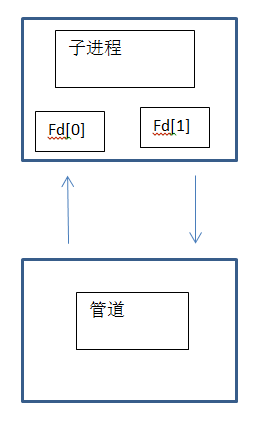
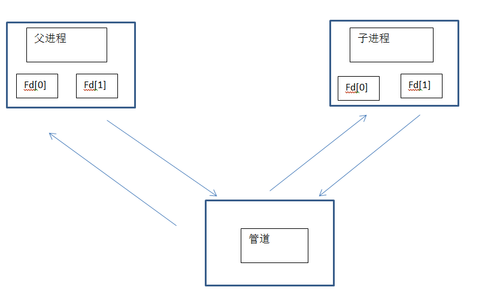
父子進程間通過管道通信。
管道只能在具有公共祖先的兩個進程間使用,通常,一個管道有另一個進程創建,在進程調用fork之後,這個管道就能在父進程和子進程之間使用了。
一般的進程,fd[0]表示讀,fd[1]表示寫。
如果有用到管道,則寫進管道,從管道讀。
父子進程之間。
所以,通過簡單的read ,write函數,把目標文件設爲fd[0] fd[1]即可以完成父子進程間的通信。
write用法,read類似。
int write(int handle, void *buf, int nbyte);
handle 是 文件描述符;
buf是指定的緩衝區,即 指針,指向一段內存單元;
nbyte是要寫入 文件指定的字節數;返回值:寫入文檔的字節數(成功);-1(出錯)
write函數把buf中nbyte寫入文件描述符handle所指的文檔,成功時返回寫的字節數,錯誤時返回-1.
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define BUFSZ 256
int main(void)
{
int fd[2];
char buf[BUFSZ];
pid_t pid;
int len;
if( pipe(fd)<0 )
{
perror("failed to pipe");
exit(1);
}
if( (pid = fork())<0 )
{
perror("failed to fork");
exit(1);
}
else if(pid > 0)
{
printf("father wrote password to pipe\n");
write(fd[1], "1234\n", 25); 父進程把password寫進後sleep,等待子進程來讀取。
sleep(1);
read(fd[0], buf, BUFSZ);
printf("father read result is %s\n", buf);
exit(0);
}
else
{
printf("child will read from pipe\n");
read(fd[0], buf, BUFSZ); 子進程從管道中讀取父進程寫進的password
printf("child read result is %s\n", buf);
printf("child wrote password to pipe\n");
write(fd[1], "4321\n", 25); 子進程把自己的password寫進,等待父進程讀取
}
return 0;
}
運行結果如下:
[root@localhost xcui]# ./pipe
father wrote password to pipe
child will read from pipe
child read result is 1234
child wrote password to pipe
father read result is 4321