Elasticsearch is an open source search engine based on Lucene, developed in Java. It provides a distributed and multitenant full-text search engine with an HTTP Dashboard web-interface (Kibana). The data is queried, retrieved and stored with a JSON document scheme. Elasticsearch is a scalable search engine that can be used to search for all kind of text documents, including log files. Elasticsearch is the heart of the 'Elastic Stack' or ELK Stack.
Logstash is an open source tool for managing events and logs. It provides real-time pipelining for data collections. Logstash will collect your log data, convert the data into JSON documents, and store them in Elasticsearch.
Kibana is an open source data visualization tool for Elasticsearch. Kibana provides a pretty dashboard web interface. It allows you to manage and visualize data from Elasticsearch. It's not just beautiful, but also powerful.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure Elastic Stack on a CentOS 7 server for monitoring server logs. Then I'll show you how to install 'Elastic beats' on a CentOS 7 and an Ubuntu 16.04 client operating system.
Prerequisites
CentOS 7 64 bit with 4GB of RAM - elk-master
CentOS 7 64 bit with 1 GB of RAM - client1
Ubuntu 16.04 64 bit with 1GB of RAM - client2
Step 1 - Prepare the Operating System
In this tutorial, we will disable SELinux on the CentOS 7 server. Edit the SELinux configuration file.
vim /etc/sysconfig/selinux
Change SELinux value from enforcing to disabled.
SELINUX=disabled
Then reboot the server.
reboot
Log in to the server again and check the SELinux state.
getenforce
Make sure the result is disabled.
Step 2 - Install Java
Java is required for the Elastic stack deployment. Elasticsearch requires Java 8, it is recommended to use the Oracle JDK 1.8. I will install Java 8 from the official Oracle rpm package.
Download Java 8 JDK with the wget command.
wget --no-cookies --no-check-certificate --header "Cookie: gpw_e24=http:%2F%2Fwww.oracle.com%2F; oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "http://download.oracle.com/otn-pub/java/jdk/8u77-b02/jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm"
Then install it with this rpm command;
rpm -ivh jdk-8u77-linux-x64.rpm
Finally, check java JDK version to ensure that it is working properly.
java -version
You will see Java version of the server.
Step 3 - Install and Configure Elasticsearch
In this step, we will install and configure Elasticsearch. I will install Elasticsearch from an rpm package provided by elastic.co and configure it to run on localhost (to make the setup secure and ensure that it is not reachable from the outside).
Before installing Elasticsearch, add the elastic.co key to the server.
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Next, download Elasticsearch 5.1 with wget and then install it.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/elasticsearch/elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.1.1.rpm
Elasticsearch is installed. Now go to the configuration directory and edit the elasticsaerch.yml configuration file.
cd /etc/elasticsearch/
vim elasticsearch.yml
Enable memory lock for Elasticsearch by removing a comment on line 40. This disables memory swapping for Elasticsearch.
bootstrap.memory_lock: true
In the 'Network' block, uncomment the network.host and http.port lines.
network.host: localhost
http.port: 9200
Save the file and exit the editor.
Now edit the elasticsearch.service file for the memory lock configuration.
vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/elasticsearch.service
Uncomment LimitMEMLOCK line.
LimitMEMLOCK=infinity
Save and exit.
Edit the sysconfig configuration file for Elasticsearch.
vim /etc/sysconfig/elasticsearch
Uncomment line 60 and make sure the value is 'unlimited'.
MAX_LOCKED_MEMORY=unlimited
Save and exit.
The Elasticsearch configuration is finished. Elasticsearch will run on the localhost IP address on port 9200, we disabled memory swapping for it by enabling mlockall on the CentOS server.
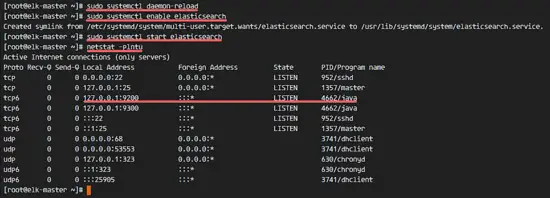
Reload systemd, enable Elasticsearch to start at boot time, then start the service.
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl enable elasticsearch
sudo systemctl start elasticsearch
Wait a second for Eelasticsearch to start, then check the open ports on the server, make sure 'state' for port 9200 is 'LISTEN'.
netstat -plntu
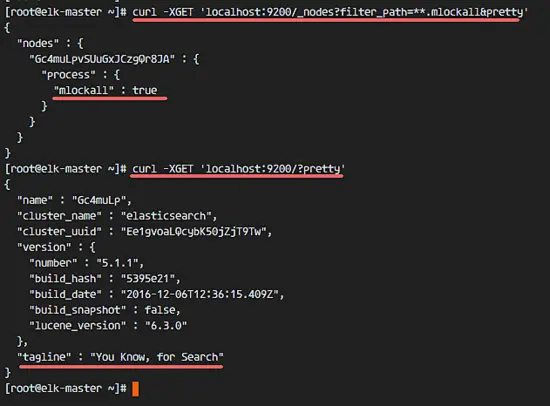
Then check the memory lock to ensure that mlockall is enabled, and check that Elasticsearch is running with the commands below.
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/_nodes?filter_path=**.mlockall&pretty'
curl -XGET 'localhost:9200/?pretty'
You will see the results below.
Step 4 - Install and Configure Kibana with Nginx
In this step, we will install and configure Kibana with a Nginx web server. Kibana will listen on the localhost IP address and Nginx acts as a reverse proxy for the Kibana application.
Download Kibana 5.1 with wget, then install it with the rpm command:
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh kibana-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
Now edit the Kibana configuration file.
vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
Uncomment the configuration lines for server.port, server.host and elasticsearch.url.
server.port: 5601
server.host: "localhost"
elasticsearch.url: "http://localhost:9200"
Save and exit.
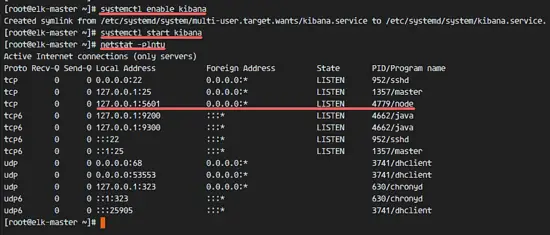
Add Kibana to run at boot and start it.
sudo systemctl enable kibana
sudo systemctl start kibana
Kibana will run on port 5601 as node application.
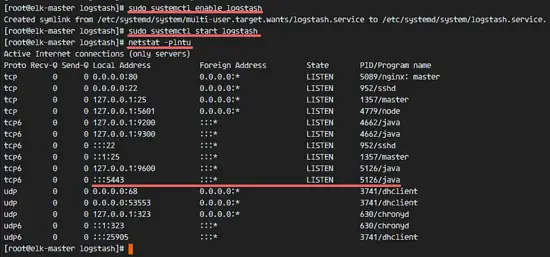
netstat -plntu
The Kibana installation is finished. Now we need to install Nginx and configure it as reverse proxy to be able to access Kibana from the public IP address.
Nginx is available in the Epel repository, install epel-release with yum.
yum -y install epel-release
Next, install the Nginx and httpd-tools package.
yum -y install nginx httpd-tools
The httpd-tools package contains tools for the web server, we will use htpasswd basic authentication for Kibana.
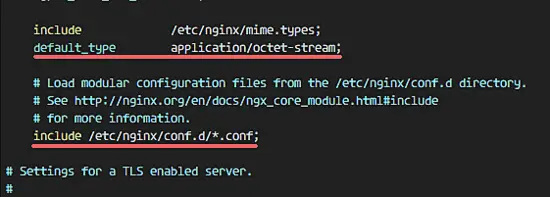
Edit the Nginx configuration file and remove the 'server { }' block, so we can add a new virtual host configuration.
cd /etc/nginx/
vim nginx.conf
Remove the server { } block.
Save the file and exit vim.
Now we need to create a new virtual host configuration file in the conf.d directory. Create the new file 'kibana.conf' with vim.
vim /etc/nginx/conf.d/kibana.conf
Paste the configuration below.
server {
listen 80;
server_name elk-stack.co;
auth_basic "Restricted Access";
auth_basic_user_file /etc/nginx/.kibana-user;
location / {
proxy_pass http://localhost:5601;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection 'upgrade';
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_cache_bypass $http_upgrade;
}
}Save and exit.
Then create a new basic authentication file with the htpasswd command.
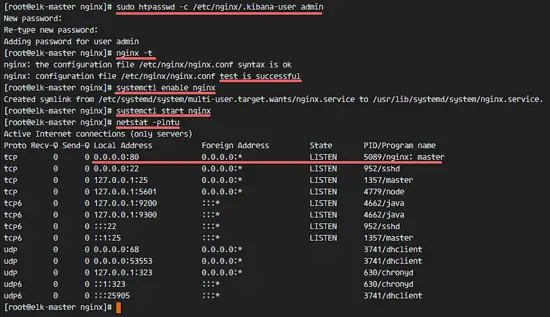
sudo htpasswd -c /etc/nginx/.kibana-user admin
TYPE YOUR PASSWORD
Test the Nginx configuration and make sure there is no error. Then add Nginx to run at the boot time and start Nginx.
nginx -t
systemctl enable nginx
systemctl start nginx
Step 5 - Install and Configure Logstash
In this step, we will install Logsatash and configure it to centralize server logs from clients with filebeat, then filter and transform the Syslog data and move it into the stash (Elasticsearch).
Download Logstash and install it with rpm.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/logstash/logstash-5.1.1.rpm
rpm -ivh logstash-5.1.1.rpm
Generate a new SSL certificate file so that the client can identify the elastic server.
Go to the tls directory and edit the openssl.cnf file.
cd /etc/pki/tls
vim openssl.cnf
Add a new line in the '[ v3_ca ]' section for the server identification.
[ v3_ca ]
# Server IP Address
subjectAltName = IP: 10.0.15.10
Save and exit.
Generate the certificate file with the openssl command.
openssl req -config /etc/pki/tls/openssl.cnf -x509 -days 3650 -batch -nodes -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key -out /etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt
The certificate files can be found in the '/etc/pki/tls/certs/' and '/etc/pki/tls/private/' directories.
Next, we will create new configuration files for Logstash. We will create a new 'filebeat-input.conf' file to configure the log sources for filebeat, then a 'syslog-filter.conf' file for syslog processing and the 'output-elasticsearch.conf' file to define the Elasticsearch output.
Go to the logstash configuration directory and create the new configuration files in the 'conf.d' subdirectory.
cd /etc/logstash/
vim conf.d/filebeat-input.conf
Input configuration: paste the configuration below.
input {
beats {
port => 5443
ssl => true
ssl_certificate => "/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"
ssl_key => "/etc/pki/tls/private/logstash-forwarder.key"
}
}Save and exit.
Create the syslog-filter.conf file.
vim conf.d/syslog-filter.conf
Paste the configuration below.
filter {
if [type] == "syslog" {
grok {
match => { "message" => "%{SYSLOGTIMESTAMP:syslog_timestamp} %{SYSLOGHOST:syslog_hostname} %{DATA:syslog_program}(?:\[%{POSINT:syslog_pid}\])?: %{GREEDYDATA:syslog_message}" }
add_field => [ "received_at", "%{@timestamp}" ]
add_field => [ "received_from", "%{host}" ]
}
date {
match => [ "syslog_timestamp", "MMM d HH:mm:ss", "MMM dd HH:mm:ss" ]
}
}
}We use a filter plugin named 'grok' to parse the syslog files.
Save and exit.
Create the output configuration file 'output-elasticsearch.conf'.
vim conf.d/output-elasticsearch.conf
Paste the configuration below.
output {
elasticsearch { hosts => ["localhost:9200"]
hosts => "localhost:9200"
manage_template => false
index => "%{[@metadata][beat]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
document_type => "%{[@metadata][type]}"
}
}Save and exit.
Finally add logstash to start at boot time and start the service.
sudo systemctl enable logstash
sudo systemctl start logstash
Step 6 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the CentOS Client
Beats are data shippers, lightweight agents that can be installed on the client nodes to send huge amounts of data from the client machine to the Logstash or Elasticsearch server. There are 4 beats available, 'Filebeat' for 'Log Files', 'Metricbeat' for 'Metrics', 'Packetbeat' for 'Network Data' and 'Winlogbeat' for the Windows client 'Event Log'.
In this tutorial, I will show you how to install and configure 'Filebeat' to transfer data log files to the Logstash server over an SSL connection.
Login to the client1 server. Then copy the certificate file from the elastic server to the client1 server.
ssh root@client1IP
Copy the certificate file with the scp command.
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
TYPE elk-server password
Create a new directory and move certificate file to that directory.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
Next, import the elastic key on the client1 server.
rpm --import https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch
Download Filebeat and install it with rpm.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh filebeat-5.1.1-x86_64.rpm
Filebeat has been installed, go to the configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml'.
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
In the paths section on line 21, add the new log files. We will add two files '/var/log/secure' for ssh activity and '/var/log/messages' for the server log.
paths:
- /var/log/secure
- /var/log/messages
Add a new configuration on line 26 to define the syslog type files.
document-type: syslog
Filebeat is using Elasticsearch as the output target by default. In this tutorial, we will change it to Logshtash. Disable Elasticsearch output by adding comments on the lines 83 and 85.
Disable elasticsearch output.
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
Now add the new logstash output configuration. Uncomment the logstash output configuration and change all value to the configuration that is shown below.
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
Save the file and exit vim.
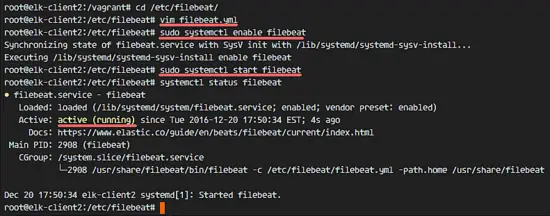
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
Step 7 - Install and Configure Filebeat on the Ubuntu Client
Connect to the server by ssh.
ssh root@ubuntu-clientIP
Copy the certificate file to the client with the scp command.
scp root@elk-serverIP:~/logstash-forwarder.crt .
Create a new directory for the certificate file and move the file to that directory.
sudo mkdir -p /etc/pki/tls/certs/
mv ~/logstash-forwarder.crt /etc/pki/tls/certs/
Add the elastic key to the server.
wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | sudo apt-key add -
Download the Filebeat .deb package and install it with the dpkg command.
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
dpkg -i filebeat-5.1.1-amd64.deb
Go to the filebeat configuration directory and edit the file 'filebeat.yml' with vim.
cd /etc/filebeat/
vim filebeat.yml
Add the new log file paths in the paths configuration section.
paths:
- /var/log/auth.log
- /var/log/syslog
Set the document type to syslog.
document-type: syslog
Disable elasticsearch output by adding comments to the lines shown below.
#-------------------------- Elasticsearch output ------------------------------
#output.elasticsearch:
# Array of hosts to connect to.
# hosts: ["localhost:9200"]
Enable logstash output, uncomment the configuration and change the values as shown below.
output.logstash:
# The Logstash hosts
hosts: ["10.0.15.10:5443"]
bulk_max_size: 1024
ssl.certificate_authorities: ["/etc/pki/tls/certs/logstash-forwarder.crt"]
template.name: "filebeat"
template.path: "filebeat.template.json"
template.overwrite: false
Save the file and exit vim.
Add Filebeat to start at boot time and start it.
sudo systemctl enable filebeat
sudo systemctl start filebeat
Check the service status.
systemctl status filebeat
Step 8 - Testing Elastic Stack
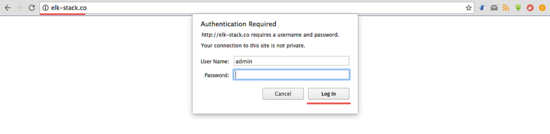
Open your web browser and visit the elastic stack domain that you used in the Nginx configuration, mine is 'elk-stack.co'. Login as admin user with your password and press Enter to log in to the Kibana dashboard.
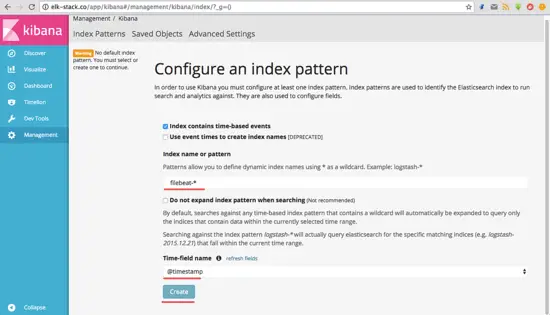
Create a new default index 'filebeat-*' and click on the 'Create' button.
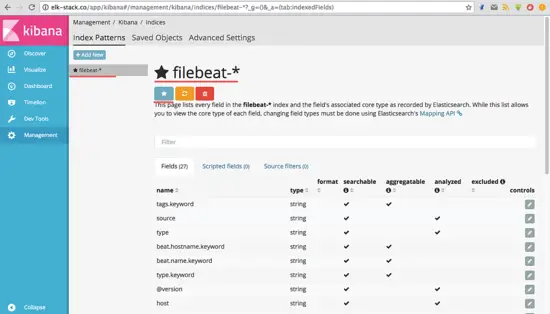
Th default index has been created. If you have multiple beats on the elastic stack, you can configure the default beat with just one click on the 'star' button.
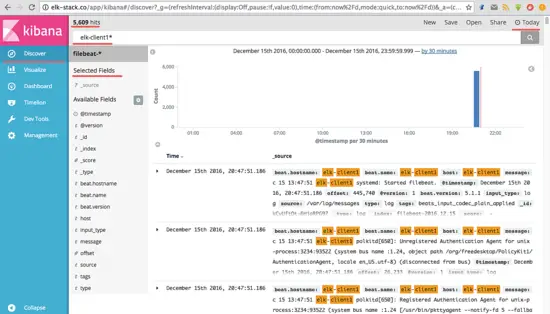
Go to the 'Discover' menu and you will see all the log file from the elk-client1 and elk-client2 servers.
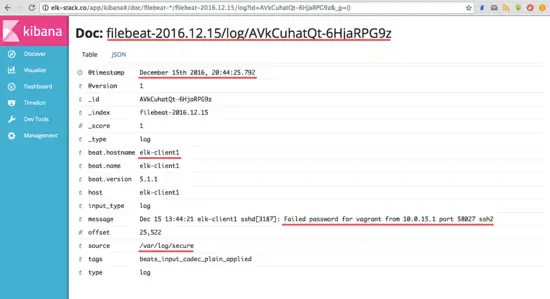
An example of JSON output from the elk-client1 server log for an invalid ssh login.
And there is much more than you can do with Kibana dashboard, just play around with the available options.
Elastic Stack has been installed on a CentOS 7 server. Filebeat has been installed on a CentOS 7 and an Ubuntu client.