iostat http://sebastien.godard.pagesperso-orange.fr/man_iostat.html
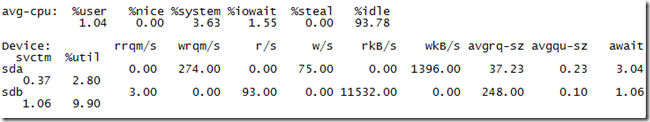
以上圖爲例查看sdb的IO情況
r/s + w/s: 就是當前的IOPS #### (93+0=93)
avgrq-sz:平均每次設備I/O操作的數據大小(扇區)#### (248.0)
avgqu-sz :平均I/O隊列長度 ####(0.10)
await:請求隊列中等待時間+svctm(服務時間) 單位是毫秒,按照每次IO平均。####(1.06)
The average time (in milliseconds) for I/O requests issued to the device to be served.
This includes the time spent by the requests in queue and the time spent servicing them.
svctm:平均每次設備I/O操作的服務時間(毫秒) ####(1.06)
svctm已經被官方註明不可信,僅供參考.因爲iostat各值基本都是計算出來的,而svctm計算方法存在錯誤的地方
The average service time (in milliseconds) for I/O requests that were issued to the device.
Warning! Do not trust this field any more. This field will be removed in a future sysstat version.
%util: (bandwidth utilization for the device)平均有百分之多少的時間用於I/O操作,或者說有多少時間I/O隊列是非空的###(9.90)
如果%util接近100%,表明I/O請求太多,I/O系統已經滿負荷,磁盤可能存在瓶頸,一般%util大於70%,I/O壓力就比較大,讀取速度有較多的wait。
注意:如果存儲設備是RAID或SSD之類的,這個說法已經不準確了
可以結合vmstat查看查看b值(等待資源的進程數)和wa值(I/O等待所佔用的CPU時間的百分比,高過30%時I/O壓力高)
Percentage of elapsed time during which I/O requests were issued to the device (bandwidth utilization for the device).
Device saturation occurs when this value is close to 100% for devices serving requests serially.
But for devices serving requests in parallel, such as RAID arrays and modern SSDs, this number does not reflect their performance limits.
avgqu-sz:(隊列長度)可作爲衡量系統I/O負荷的指標, 超過處理能力的請求數目,待處理的 I/O 請求,當請求持續超出磁盤處理能力,該值將增加。
但由於avcqu-sz是按照單位時間的平均值,所以不能反映瞬間的I/O洪水。應結合參考svctm.以及r/s及w/s。
svctm的大小一般和磁盤性能有關,CPU/內存的負荷也會對其有影響,請求過多也會間接導致svctm的增加。
await的大小一般取決於服務時間(svctm)以及I/O隊列的長度和I/O請求的發出模式。
如果await比較接近svctm,說明I/O幾乎沒有等待時間;如果await遠大於svctm,說明I/O隊列太長,應用得到的響應時間變慢,
如果響應時間超過了用戶可以容許的範圍,這時可以考慮更換更快的磁盤,調整內核elevator算法,優化應用,或者升級CPU