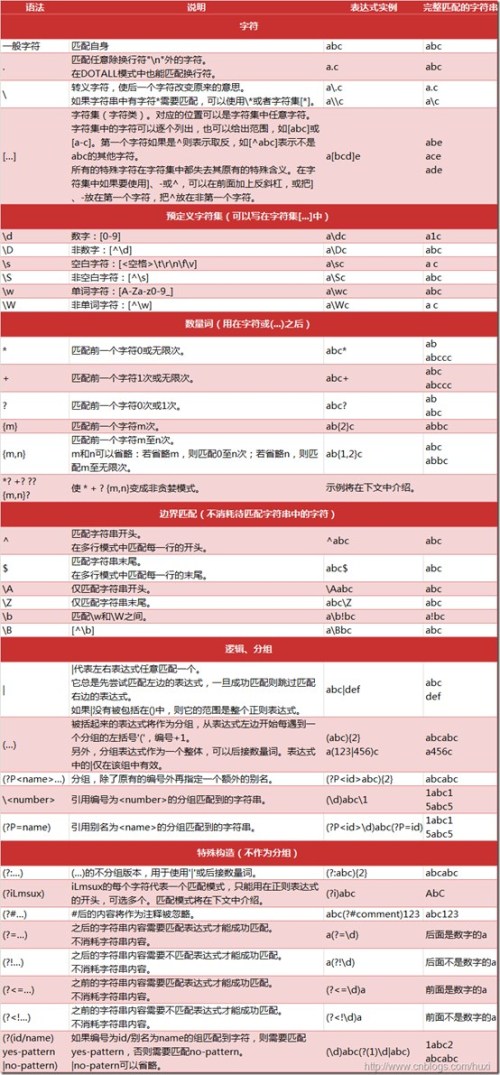
python常用正则表达式规则表
图片来自CSDN
正则匹配中r含义
r表示raw的简及raw string 意思是原生字符,也就是说是这个字符串中间的特殊字符不用转义。比如你要表示‘\n’,可以这样:r'\n'。但是如果你不用原生字符 而是用字符串你得这样:‘\\n’
re模块的使用
使用Python中的re模块,将正则表达式编译为正则对象,提升代码的执行效率
例子:
import timeit
#将正则表达式赋值给reg变量,后面使用match方法调用该对象
print (timeit.timeit(setup='''import re; reg = re.compile('<(?P<tagname>\w*)>.*</(?P=tagname)>')''', stmt='''reg.match('<h1>xxx</h1>')''', number=1000000))
#每次都要先调用正则表达式
print (timeit.timeit(setup='''import re''', stmt='''re.match('<(?P<tagname>\w*)>.*</(?P=tagname)>', '<h1>xxx</h1>')''', number=1000000))
输出:
3.2538992546554226
7.934942773753158
re.compile(pattern[, flags])使用
这个方法是就是将字符串的正则表达式编译为正则对象,第二个参数flag是匹配模式,取值可以使用按位或者运算符“|”表示同时生效,比如:re.I | re.M,flag的可选值有:
re.I(re.IGNORECASE): 忽略大小写(括号内是完整写法,下同)
M(MULTILINE): 多行模式,改变'^'和'$'的行为
S(DOTALL): 点任意匹配模式,改变'.'的行为
L(LOCALE): 使预定字符类 \w \W \b \B \s \S 取决于当前区域设定
U(UNICODE): 使预定字符类 \w \W \b \B \s \S \d \D 取决于unicode定义的字符属性
X(VERBOSE): 详细模式。这个模式下正则表达式可以是多行,忽略空白字符,并可以加入注释。以下两个正则表达式是等价的:
a = re.compile(r"""\d + # the integral part
\. # the decimal point
\d * # some fractional digits""", re.X)
b = re.compile(r"\d+\.\d*")
match方法
match(string[, pos[, endpos]])
string:匹配使用的文本,
pos: 文本中正则表达式开始搜索的索引。及开始搜索string的下标
endpos: 文本中正则表达式结束搜索的索引。
如果不指定pos,默认是从开头开始匹配,如果匹配不到,直接返回None
例子:
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'\w*(hello w.*)(hellol.*)')
result = pattern.match(r'aahello worldhello ling')
print(result)
result2 = pattern.match(r'hello world helloling')
print(result2.groups())
输出:
None
('hello world ', 'hello ling')
我们可以看到result1已经由字符串转换成了一个正则对象。rangeesule.groups()可以查看出来所有匹配到的数据,每个()是一个元素,最终返回一个tuple。group()既可以通过下标(从1开始)的方式访问,也可以通过分组名进行访问。groupdict只能显示有分组名的数据。
例子2:
import re
prog = re.compile(r'(?P<tagname>abc)(.*)(?P=tagname)')
result1 = prog.match('abclfjlad234sjldabc')
print(result1)
print(result1.groups())
print result1.group('tagname')
print(result1.group(2))
print(result1.groupdict())
输出:
<_sre.SRE_Match object at 0x0000000002176E88>
('abc', 'lfjlad234sjld')
abc
lfjlad234sjld
{'tagname': 'abc'}
search方法
不建议使用search方法,search方法相较match方法效率低下
例子:
import re
pattern = re.compile(r'(hello w.*)(hellol.*)')
result1 = pattern.search(r'aahello worldhello ling')
print(result1.groups())
输出:
('hello world ', 'hello ling')
spilt方法
split(string[, maxsplit])
按照能够匹配的子串将string分割后返回列表。maxsplit用于指定最大分割次数,不指定将全部分割。
例子:
import re
p = re.compile(r'\d+')
print(p.split('one1two2three3four4'))
输出:
['one', 'two', 'three', 'four', '']
findall方法
findall(string[, pos[, endpos]])
搜索string,以列表形式返回全部能匹配的子串.
例子:
import re
p = re.compile(r'\d+')
print(findall('one1two2three3four4'))
输出:
['1', '2', '3', '4']
findditer方法
finditer(string[, pos[, endpos]])
搜索string,返回一个顺序访问每一个匹配结果(Match对象)的迭代器。
例子:
import re
p = re.compile(r'\d+')
print(type(p.finditer('one1two2three3four4')))
for m in p.finditer('one1two2three3four4'):
print(type(m))
print(m.group())
输出:
<type 'callable-iterator'>
<type '_sre.SRE_Match'>
1
<type '_sre.SRE_Match'>
2
<type '_sre.SRE_Match'>
3
<type '_sre.SRE_Match'>
4
sub方法
sub(repl, string[, count])
使用repl替换string中每一个匹配的子串后返回替换后的字符串。
当repl是一个字符串时,可以使用\id或\g<id>、\g<name>引用分组,但不能使用编号0。
当repl是一个方法时,这个方法应当只接受一个参数(Match对象),并返回一个字符串用于替换(返回的字符串中不能再引用分组)。
count用于指定最多替换次数,不指定时全部替换。
例子:
import re
p = re.compile(r'(\w+) (\w+)')
s = 'i say, hello world!'
print(p.sub(r'\2 \1', s))
def func(m):
return m.group(1).title() + ' ' + m.group(2).title()
print(p.sub(func, s))
输出:
say i, world hello!
I Say, Hello World!