1.RDD基礎:
Spark中RDD是不可變的分佈式對象集合。每個RDD被分爲多個分區,這些分區運行在集羣中的不同節點上。RDD可以包含任意類型的對象(甚至可以是自定義的)。
前面講到,Spark包含轉化操作和行動操作。Spark只會惰性計算這些RDD。它們只有第一次在一個行動操作中用到時,纔會真正計算。默認情況下,Spark的RDD會在你每次對它們進行行動操作時重新計算。如果想在多個行動操作中重用同一個RDD,可以使用RDD.persist()讓Spark把這個RDD緩存(內存或者磁盤)下來。
2.創建RDD:
Spark提供2種創建方式:
(1)讀取外部數據集:之前的sc.textFile()就屬於這種類型。更加常用的方式。
(2)在驅動器程序中對一個集合(list、Set等)進行並行化,要使用SparkContext.parallelize()方法。
3.RDD操作:
RDD主要分成數據類型RDD和鍵值對RDD。有一些操作可以適用於所有類型的RDD,這時候可以直接創建JavaRDD對象,例如map(),filter()等。有些操作只適用於數據類型的RDD,例如 ,這時候創建JavaDoubleRDD對象。有些操作只適用於鍵值對RDD,例如 ,這時候創建JavaPairRDD對象。
3.1 轉化操作:
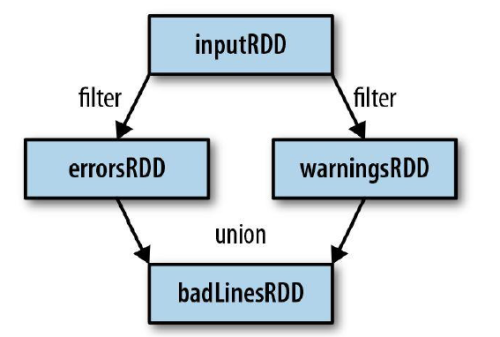
3.1.1 譜系圖:
通過轉化操作,從已有的RDD中派生出新的RDD,Spark會使用譜系圖來記錄這些不同RDD之間的依賴關係。如下圖所示:
3.1.2 :
基本的轉化操作(map、flatMap、filter、distinct、sample),假設RDD的數據{1, 2, 3, 3}:
RDD的集合操作(union、intersection、subtract、cartesian),兩個RDD分別是{1,2,3}、{3,4,5}:
| 函數名 | 作用 | 例子 | 運行結果 |
| map() | Apply a function to each element in the RDD and return an RDD of the result. | rdd.map(x => x +1) | {2, 3, 4, 4} |
| flatMap() | Apply a function to each element in the RDD and return an RDD of the contents of the iterators returned. Often used to extract words. | rdd.flatMap(x =>x.to(3)) | {1, 2, 3, 2, 3, 3, 3} |
| filter() | Return an RDD consisting of only elements that pass the condition passed to filter(). | rdd.filter(x => x!= 1) | {2, 3, 3} |
| distinct() | Remove duplicates. | rdd.distinct() | {1, 2, 3} |
| sample(withReplacement,fraction, [seed]) | Sample an RDD, with or without replacement. | rdd.sample(false,0.5) | 不確定 |
| union() | Produce an RDD containing elements from both RDDs. | rdd.union(other) | {1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5} |
| intersection() | RDD containing only elements found in both RDDs. | rdd.intersection(other) | {3} |
| subtract() | Remove the contents of one RDD (e.g., remove training data). | rdd.subtract(other) | {1, 2} |
| cartesian() | Cartesian product with the other RDD. | rdd.cartesian(other) | {(1, 3), (1, 4),… (3, 5)} |
4.給Spark傳遞函數:
大多數的轉化操作和一部分行動操作,都需要給Spark方法傳遞函數。在java中,函數式實現了包org.apache.spark.api.java.function下面任意一個接口的類。該包下面有許多接口,下面是一些基礎接口:
| 函數名 | 需要實現的方法 | 用法 |
| Function<T, R> | R call(T) | Take in one input and return one output, for use with operations like map()and filter(). |
Function2<T1, T2,R> | R call(T1, T2) | Take in two inputs and return one output, for use with operations like aggregate() or fold(). |
| FlatMapFunction<T,R> | Iterable<R> call(T) | Take in one input and return zero or more outputs, for use with operations like flatMap(). |