Python標準庫系列之Redis模塊
What is redis?
Redis is an open source (BSD licensed), in-memory data structure store, used as database, cache and message broker. It supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets with range queries, bitmaps, hyperloglogs and geospatial indexes with radius queries. Redis has built-in replication, Lua scripting, LRU eviction, transactions and different levels of on-disk persistence, and provides high availability via Redis Sentinel and automatic partitioning with Redis Cluster.
Redis官網:http://redis.io/
以上摘自官網介紹
安裝Redis
安裝
模塊GitHub地址:https://github.com/WoLpH/redis-py
[root@anshengme ~]# yum -y install redis
配置綁定的IP
[root@anshengme ~]# vim /etc/redis.conf bind 0.0.0.0
啓動並設置開機自啓動
[root@anshengme ~]# systemctl start redis [root@anshengme ~]# systemctl enable redis Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/redis.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/redis.service.
檢查
查看端口
[root@anshengme ~]# netstat -tlnp | grep "redis" tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1439/redis-server 0
數據寫入測試
[root@anshengme ~]# /usr/bin/redis-cli 127.0.0.1:6379> set url https://blog.ansheng.me OK 127.0.0.1:6379> get url "https://blog.ansheng.me" 127.0.0.1:6379> exit
安裝redis-py
安裝redis-py
pip3 install redis
或源碼安裝
python setup.py install
檢查安裝是否成功
# 導入模塊沒報錯則安裝成功 >>> import redis
入門及使用
# 導入模塊
>>> import redis
# 連接到Redis服務器
>>> conn = redis.Redis(host='192.168.56.100', port=6379)
# 寫入一條數據
>>> conn.set('name','ansheng')
True
# 獲取一條數據
>>> conn.get('name')
b'ansheng'
>>> conn.get('url')
b'https://blog.ansheng.me'使用連接池連接到Redis
Behind the scenes, redis-py uses a connection pool to manage connections to a Redis server. By default, each Redis instance you create will in turn create its own connection pool. You can override this behavior and use an existing connection pool by passing an already created connection pool instance to the connection_pool argument of the Redis class. You may choose to do this in order to implement client side sharding or have finer grain control of how connections are managed.
>>> pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.56.100', port=6379)
>>> conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
>>> conn.set('hello','world')
True
>>> conn.get('hello')
b'world'使用套接字連接
>>> r = redis.Redis(unix_socket_path='/tmp/redis.sock')
API
redis-py提供的API用來操作redis
String API
set(name, value, ex=None, px=None, nx=False, xx=False)
| 參數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
ex | 過期時間(秒) |
px | 過期時間(毫秒) |
nx | 如果設置爲True,則只有name不存在時,當前set操作才執行 |
xx | 如果設置爲True,則只有name存在時,崗前set操作才執行 |
>>> conn.set('k1', 'v1', ex=10, nx=True)
True
>>> conn.get('k1')
b'v1'
>>> conn.get('k1')setex(name, value, time)
設置過期時間/秒
>>> conn.setex('k','v',1)
True
>>> conn.get('k')psetex(name, time_ms, value)
設置過期時間/毫秒
>>> conn.psetex('k',10,'v')
True
>>> conn.get('k')setnx(name, value)
設置值,只有key不存在時,執行設置操作
>>> conn.get('k1')
>>> conn.setnx('k1','v1')
True
>>> conn.get('k1')
b'v1'
>>> conn.setnx('k2','v2')
Falsemset(*args, **kwargs)
同時設置多個key/value
>>> conn.mset(k1='v1', k2='v2')
True
>>> conn.mset({'k1':'v1', 'k1':'v1'})
Trueget(name)
獲取單個值
>>> conn.get('k1')
b'v1'mget(keys, *args)
獲取多個值
>>> conn.mget('k1','k2')
[b'v1', b'v2']
# 傳入列表
>>> conn.mget(['name','url'])
[b'ansheng', b'https://blog.ansheng.me']getset(name, value)
設置新值並獲取原來的值
>>> conn.set('hello', 'world')
True
>>> result = conn.getset('hello', 'Linux')
>>> result
b'world'
>>> conn.get('hello')
b'Linux'getrange(key, start, end)
通過索引的方式來獲取value的值
>>> conn.set('key','value')
True
>>> conn.getrange('key', 1, 4)
b'alue'setrange(name, offset, value)
根據索引修改value
>>> conn.set('n','123456789')
True
>>> conn.setrange('n', 0, 'a')
9
>>> conn.get('n')
b'a23456789setbit(name, offset, value)
getbit(name, offset)
獲取value對應某一個索引位置對應的值0/1
>>> conn.getbit('k',1)
1bitcount(key, start=None, end=None)
獲取key對應二進制中表示1的個數
bitop(operation, dest, *keys)
將多個值進行值運算,得出的結果保存到一個新值當中
>>> conn.mset(n1='abc',n2='cde',n3='adc')
True
>>> conn.bitop('AND','now_key','n1','n2','n3')
3
>>> conn.get('now_key')
b'a`a'
>>> conn.mget('n1','n2','n3')
[b'abc', b'cde', b'adc']operation支持AND(並)、OR(或)、NOT(非)、XOR(異或)
strlen(name)
獲取value的長度
>>> conn.set('name','安生')
True
>>> conn.strlen('name')
6incr(name, amount=1)
對name的value進行自增,如果name不存在則創建,否則自增
>>> conn.get('number')
>>> conn.incr('number')
1
>>> conn.get('number')
b'1'
>>> conn.incr('number')
2
>>> conn.incr('number', 10)
12incrbyfloat(name, amount=1.0)
同上,支持浮點數自增
>>> conn.incrbyfloat('number', 1.5)
13.5
>>> conn.incrbyfloat('number', 1.1)
14.6decr(name, amount=1)
自減,同自增一樣,如果進行自減的value不是整數就報錯
>>> conn.set('n', 10)
True
>>> conn.decr('n')
9
>>> conn.decr('n', 9)
0append(key, value)
在value後面追加內容
>>> conn.set('blog','https://blog.ansheng.me')
True
>>> conn.append('blog','/')
26
>>> conn.get('blog')
b'https://blog.ansheng.me/'Hash API
hset(name, key, value)
設置name的鍵值對,有則修改,沒有則創建
>>> conn.hset('dic','k1','v1')
1
>>> conn.hget('dic','k1')
b'v1'hmset(name, mapping)
同時設置多個name的key/value
>>> conn.hmset('dic', {'k1': 'v1', 'k2': 'v2'})
True
>>> conn.hget('dic','k2')
b'v2'hget(name, key)
獲取name中key的值
>>> conn.hget('dic','k2')
b'v2'hmget(name, keys, *args)
同時獲取多個
>>> conn.hmget('dic',['k1', 'k2'])
[b'v1', b'v2']
>>> conn.hmget('dic','k1', 'k2')
[b'v1', b'v2']hgetall(name)
獲取name對應的所有key/value
>>> conn.hgetall('dic')
{b'k1': b'v1', b'k2': b'v2'}hlen(name)
獲取name對應鍵值對的個數
>>> conn.hlen('dic')
2hkeys(name)
獲取name中所有的key
>>> conn.hkeys('dic')
[b'k1', b'k2']hvals(name)
獲取name中所有的value
>>> conn.hvals('dic')
[b'v1', b'v2']hexists(name, key)
檢查當前name中是否有傳入的key
>>> conn.hexists('dic','k1')
True
>>> conn.hexists('dic','kk')
Falsehdel(self, name, *keys)
刪除name中對應的key
>>> conn.hdel('dic','k1')
1
>>> conn.hget('dic','k1')hincrby(name, key, amount=1)
name中key對應的value進行自增,如果不存在則創建
>>> conn.hincrby('dic','number')
1
>>> conn.hincrby('dic','number',10)
11hincrbyfloat(name, key, amount=1.0)
value自增,支持浮點數,同上
>>> conn.hincrbyfloat('dic','float')
1.0
>>> conn.hincrbyfloat('dic','float',0.3)
1.3hscan(name, cursor=0, match=None, count=None)
增量式迭代獲取,hscan可以實現分片的獲取數據,並非一次性將數據全部獲取完,從而放置內存被撐爆
| 參數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
name | redis的name |
cursor | 遊標(基於遊標分批取獲取數據) |
match | 匹配指定key,默認None 表示所有的key |
count | 每次分片最少獲取個數,默認None表示採用Redis的默認分片個數 |
hscan_iter(name, match=None, count=None)
利用yield封裝hscan創建生成器,實現分批去redis中獲取數據
| 參數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
match | 匹配指定key,默認None 表示所有的key |
count | 每次分片最少獲取個數,默認None表示採用Redis的默認分片個數 |
如:
for item in r.hscan_iter('xx'):
print itemexpire(name, time)
設置過期時間
>>> conn.hset('info','BlogUrl','https://blog.ansheng.me')
1
>>> conn.expire('info', 10)
True
>>> conn.hget('info','BlogUrl')
b'https://blog.ansheng.me'
>>> conn.hget('info','BlogUrl')ListAPI
lpush(name, *values)
在最左邊添加值
>>> conn.lpush('li', 11,22,33)
3
>>> conn.lindex('li', 0)
b'33'rpush(name, *values)
在最右邊添加值
>>> conn.rpush('lli', 11,22,33)
3
>>> conn.lindex('lli', 0)
b'11'lpushx(name, value)
只有name已經存在時,值添加到列表的最左邊
>>> conn.lpushx('li', 'aa')
4
>>> conn.lindex('li', 0)
b'aa'rpushx(name, value)
只有name已經存在時,值添加到列表的最右邊
>>> conn.rpushx('li', 'bb')
5
>>> conn.lindex('li', 0)
b'aa'
>>> conn.lindex('li', 4)
b'bb'llen(name)
獲取name元素的個數
>>> conn.llen('li')
5linsert(name, where, refvalue, value)
在name的某一個值前面或者後面插入一個新值
>>> conn.linsert('li','AFTER','11','cc')
6
>>> conn.lindex('li', 3)
b'11'
>>> conn.lindex('li', 4)
b'cc'lset(name, index, value)
對name中index索引位置的值進行重新賦值
>>> conn.lindex('li', 4)
b'cc'
>>> conn.lset('li', 4, 'hello')
True
>>> conn.lindex('li', 4)
b'hello'lrem(name, value, num=0)
刪除指定value後面或者前面的值
num=2,從前到後,刪除2個;
num=-2,從後向前,刪除2個
>>> conn.llen('li')
6
>>> conn.lrem('li', 'hello')
1
>>> conn.llen('li')
5
>>> conn.lrem('li', '22', num=2)
2
>>> conn.llen('li')
3lpop(name)
刪除name中左側第一個元素
>>> conn.lindex('li', 0)
b'11'
>>> conn.lpop('li')
b'11'rpop(name)
刪除name中右側第一個元素
>>> conn.rpop('li')
b'33lindex(name, index)
獲取name中對應索引的值
>>> conn.lindex('li', 0)
b'aa'lrange(name, start, end)
使用切片獲取數據
>>> conn.llen('li')
8
>>> conn.lrange('li',0,5)
[b'3', b'23', b'34', b'235', b'2', b'1']ltrim(name, start, end)
在name對應的列表中移除沒有在start-end索引之間的值
>>> conn.ltrim('li',0,5)
True
>>> conn.llen('li')
6rpoplpush(src, dst)
從src列表中取出最右邊的元素,同時將其添加至dst列表的最左邊
>>> conn.lpush('li1', 1,2,3)
3
>>> conn.lpush('li2', 'a','b','c')
3
>>> conn.rpoplpush('li1','li2')
b'1'blpop(keys, timeout=0)
brpop(keys, timeout=0)
brpoplpush(src, dst, timeout=0)
從src列表的右側移除一個元素並將其添加到dst列表的左側
>>> conn.lpush('ll', 'a','b','c')
3
>>> conn.lpush('aa', 'a','b','c')
3
>>> conn.brpoplpush('ll','aa')
b'a'timeout,當src對應的列表中沒有數據時,阻塞等待其有數據的超時時間(秒),0 表示永遠阻塞
自定義增量迭代
由於redis類庫中沒有提供對列表元素的增量迭代,如果想要循環name對應的列表的所有元素,那麼就需要:
獲取name對應的所有列表
循環列表
但是,如果列表非常大,那麼就有可能在第一步時就將程序的內容撐爆,所有有必要自定義一個增量迭代的功能:
def list_iter(name): """ 自定義redis列表增量迭代 :param name: redis中的name,即:迭代name對應的列表 :return: yield 返回 列表元素 """ list_count = r.llen(name) for index in xrange(list_count): yield r.lindex(name, index)
使用
for item in list_iter('pp'):
print itemSET API
sadd(name, *values)
爲name添加值,如果存在則不添加
>>> conn.sadd('s1', 1)
1
>>> conn.sadd('s1', 1)
0scard(name)
返回name的元素數量
>>> conn.scard('s1')
1sdiff(keys, *args)
在keys集合中不在其他集合中的數據
>>> conn.sdiff('s1','s2')
{b'c', b'v', b'a'}sdiffstore(dest, keys, *args)
在keys集合中不在其他集合中的數據保存到dest集合中
>>> conn.sdiffstore('news','s1','s2')
3
>>> conn.scard('news')
3sinter(keys, *args)
獲取keys集合中與其他集合中的並集
>>> conn.sinter('s1','s2')
{b'2', b'3', b'1'}sinterstore(dest, keys, *args)
獲取keys集合中與其他集合中的並集數據並保存到dest集合中
>>> conn.sinterstore('news1','s1','s2')
3sismember(name, value)
獲取value是否是name集合中的成員
>>> conn.sismember('news1','1')
True
>>> conn.sismember('news1','aa1')
Falsesmembers(name)
獲取name集合中所有的成員
>>> conn.smembers('news1')
{b'2', b'3', b'1'}smove(src, dst, value)
將src中的value移動到dst中
>>> conn.smembers('s1')
{b'c', b'2', b'v', b'1', b'3', b'a'}
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'2', b'3', b'1'}
>>> conn.smove('s1','s2','v')
True
>>> conn.smembers('s1')
{b'c', b'2', b'a', b'3', b'1'}
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'2', b'v', b'3', b'1'}spop(name)
刪除並返回name中的隨機成員
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'2', b'v', b'3', b'1'}
>>> conn.spop('s2')
b'3'
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'2', b'v', b'1'}
>>> conn.spop('s2')
b'2'
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'v', b'1'}
>>> conn.spop('s2')
b'1'
>>> conn.smembers('s2')
{b'v'}srandmember(name, number=None)
隨機獲取name集合中的number個成員,默認number=1
>>> conn.smembers('s1')
{b'c', b'2', b'a', b'3', b'1'}
>>> conn.srandmember('s1')
b'1'
>>> conn.srandmember('s1')
b'a'
>>> conn.srandmember('s1',number=2)
[b'3', b'a']
>>> conn.srandmember('s1',number=2)
[b'1', b'2']srem(name, *values)
刪除name集合中的values數據
>>> conn.smembers('s1')
{b'c', b'2', b'a', b'3', b'1'}
>>> conn.srem('s1','1','2')
2
>>> conn.smembers('s1')
{b'c', b'a', b'3'}sunion(keys, *args)
獲取keys集合與其他集合的並集
>>> conn.sadd('a1',1,2,3)
3
>>> conn.sadd('a2',1,2,3,4,5,6,7)
7
>>> conn.sunion('a2','a1')
{b'2', b'7', b'1', b'3', b'6', b'5', b'4'}sunionstore(dest, keys, *args)
獲取keys集合與其他集合的並集並保存到dest中
>>> conn.sunionstore('a3', 'a2','a1')
7
>>> conn.smembers('a3')
{b'2', b'7', b'1', b'3', b'6', b'5', b'4'}Ordered set API
zadd(name, *args, **kwargs)
>>> conn.zadd('h1','n1',11,'n2',22)
2
>>> conn.zadd('h2',n1=11,n2=22)
2zcard(name)
返回有序集合name元素的數量
>>> conn.zcard('h1')
2zcount(name, min, max)
返回在name中值在min與max之間的值個數
>>> conn.zcount('h1',10,30)
2zincrby(name, value, amount=1)
name中讓value的值加上amount
>>> conn.zincrby('h1','n1',10)
21.0zinterstore(dest, keys, aggregate=None)
zlexcount(name, min, max)
zrange(name, start, end, desc=False, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float)
| 參數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
name | redis的name |
start | 有序集合索引起始位置(非分數) |
end | 有序集合索引結束位置(非分數) |
desc | 排序規則,默認按照分數從小到大排序 |
withscores | 是否獲取元素的分數,默認只獲取元素的值 |
score_cast_func | 對分數進行數據轉換的函數 |
>>> conn.zrange('h1', 1, 2, desc=True, withscores=True, score_cast_func=float)
[(b'n1', 21.0)]
>>> conn.zrange('h1', 1, 2, desc=False, withscores=True, score_cast_func=float)
[(b'n2', 22.0)]# 從大到小排序 zrevrange(name, start, end, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float) # 按照分數範圍獲取name對應的有序集合的元素 zrangebyscore(name, min, max, start=None, num=None, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float) # 從大到小排序 zrevrangebyscore(name, max, min, start=None, num=None, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float)
zrangebylex(name, min, max, start=None, num=None)
當有序集合的所有成員都具有相同的分值時,有序集合的元素會根據成員的 值 (lexicographical ordering)來進行排序,而這個命令則可以返回給定的有序集合鍵 key 中, 元素的值介於 min 和 max 之間的成員
對集合中的每個成員進行逐個字節的對比(byte-by-byte compare), 並按照從低到高的順序, 返回排序後的集合成員。 如果兩個字符串有一部分內容是相同的話, 那麼命令會認爲較長的字符串比較短的字符串要大
| 參數 | 描述 |
|---|---|
name | redis的name |
min | 左區間(值) + 表示正無限; - 表示負無限; ( 表示開區間; [ 則表示閉區間 |
min | 右區間(值) |
start | 對結果進行分片處理,索引位置 |
num | 對結果進行分片處理,索引後面的num個元素 |
如:
ZADD myzset 0 aa 0 ba 0 ca 0 da 0 ea 0 fa 0 ga
# r.zrangebylex('myzset', "-", "[ca") 結果爲:['aa', 'ba', 'ca']更多:
# 從大到小排序 zrevrangebylex(name, max, min, start=None, num=None)
zrevrangebylex(name, max, min, start=None, num=None)
zrangebyscore(name, min, max, start=None, num=None, withscores=False, score_cast_func=float)**
zrank(name, value)
返回基於0的值,指示在排序集名稱的值排名
>>> conn.zrank('h1','n1')
0
>>> conn.zrank('h1','n2')
1zrevrank(name, value),從大到小排序
zrem(name, *values)
刪除name中對應的values
>>> conn.zrem('h1','n2')
1
>>> conn.zrem('h2',['n1','n2'])
2zremrangebyrank(name, min, max)
根據排行範圍進行刪除
>>> conn.zremrangebyrank('h1',1,2)
1zremrangebyscore(name, min, max)
根據分數範圍進行刪除
>>> conn.zremrangebyscore('h1',10,20)
2zscore(name, value)
返回指定value的值是多少
>>> conn.zscore('h1','n1')
11.0zunionstore(dest, keys, aggregate=None)
Global API
delete(*names)
在redis中刪除names
>>> conn.delete('ooo')
1exists(name)
檢測name是否存在
>>> conn.exists('iii')
False
>>> conn.exists('h1')
Truekeys(pattern=’*’)
# 匹配數據庫中所有 key >>> conn.keys(pattern='*') [b'h2', b'kasd1', b'n2', b'url', b'name', b'n', b'li1', b'n1', b's1', b'now_key', b'l', b's2', b'number', b'numbers', b'a2', b'dic', b'a1', b'news', b'news1', b'aa', b'key', b'lli', b'll', b'k', b'li', b'k2', b'h1', b'li2', b'ccc', b'k1', b'blog', b'kaasdsd1', b'a3', b'l1', b'l2', b'n3', b'a']
# 匹配hello,hallo和hxllo等 conn.keys(pattern='h?llo') # 匹配hllo和heeeeello 等 conn.keys(pattern='h*llo') # 匹配hello和hallo,但不匹配 hillo conn.keys(pattern='h[ae]llo')
rename(src, dst)
把src重命名成dst
>>> conn.set('k','v')
True
>>> conn.get('k')
b'v'
>>> conn.rename('k', 'kk')
True
>>> conn.get('k')
>>> conn.get('kk')
b'v'move(name, db)
將redis的某個值移動到指定的db下
randomkey()
隨機獲取一個redis的name,不進行刪除
>>> conn.randomkey() b'll' >>> conn.randomkey() b'news1'
type(name)
查看name的類型
>>> conn.type('kk')
b'string'管道
redis-py默認在執行每次請求都會創建(連接池申請連接)和斷開(歸還連接池)一次連接操作,如果想要在一次請求中指定多個命令,則可以使用pipline實現一次請求指定多個命令,並且默認情況下一次pipline 是原子性操作(MySQL中的事務)。
>>> import redis
>>> pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.56.100', port=6379)
>>> r = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
# 創建一個通道支持事務
>>> pipe = r.pipeline(transaction=True)
#
>>> r.set('hello', 'world')
True
>>> r.set('blog', 'ansheng.me')
True
# 如果在設置上面兩個值的過程中出錯了,那麼這次提交就不會執行
>>> pipe.execute()
[]發佈訂閱
# monitor.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import redis
class RedisHelper:
def __init__(self):
self.__conn = redis.Redis(host='192.168.56.100')
self.chan_sub = 'fm104.5'
self.chan_pub = 'fm104.5'
def public(self, msg):
self.__conn.publish(self.chan_pub, msg)
return True
def subscribe(self):
pub = self.__conn.pubsub()
pub.subscribe(self.chan_sub)
pub.parse_response()
return pub
# subscriber.py 訂閱者
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from monitor import RedisHelper
obj = RedisHelper()
redis_sub = obj.subscribe()
while True:
msg = redis_sub.parse_response()
print(msg)
# announcer.py 發佈者
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from monitor import RedisHelper
obj = RedisHelper()
obj.public('hello')實例
讓redis緩存tornado頁面
# _*_coding:utf-8 _*_
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import time
import redis
poll = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.56.100', port=6379)
conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=poll)
class MainHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def get(self):
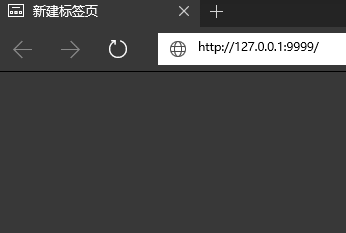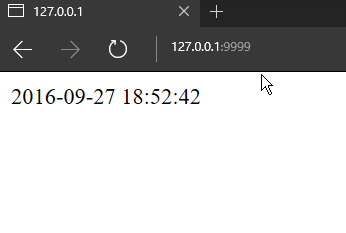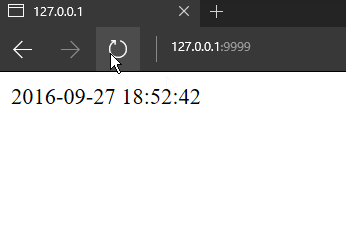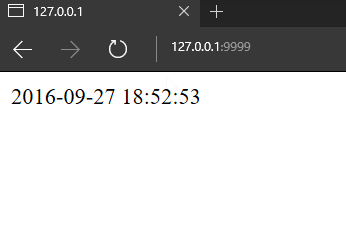
CurrentTim = conn.get('CurrentTim')
if CurrentTim:
self.write(CurrentTim)
else:
CurrentTim = time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S', time.localtime(time.time()))
conn.set('CurrentTim', CurrentTim, ex=5)
self.write(CurrentTim)
settings = {
"tempalte_path": "template",
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r'/', MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(9999)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()基於Redis的Session存儲
app.py
# _*_coding:utf-8 _*_
import tornado.ioloop
import tornado.web
import RedisToSession
class BaseHandler(tornado.web.RequestHandler):
def initialize(self):
self.session = RedisToSession.Session(self)
class MainHandler(BaseHandler):
def get(self):
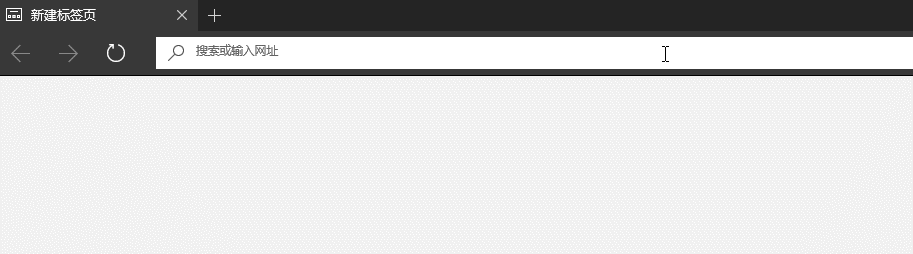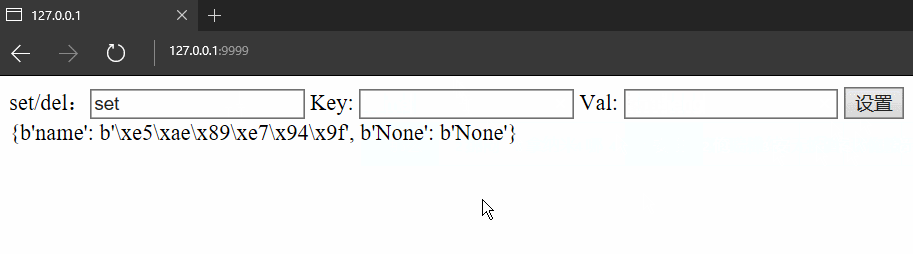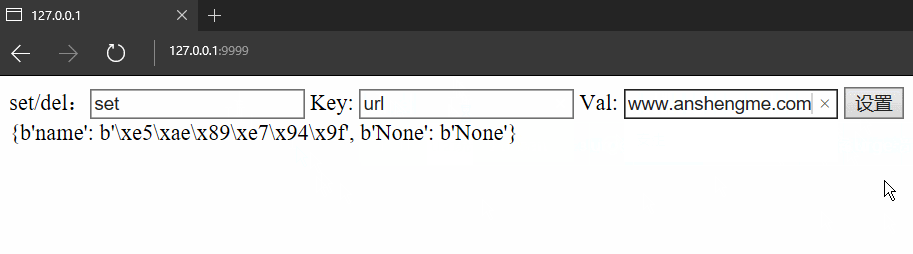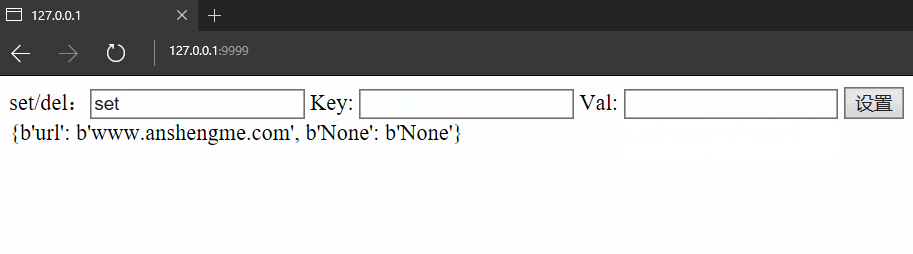
Info = self.session.GetAll()
self.render("template/index.html", Data=Info)
def post(self, *args, **kwargs):
# 獲取傳過來的值
Key = self.get_argument('key')
Val = self.get_argument('val')
action = self.get_argument('action')
if action == 'set':
# 設置值
self.session[Key] = Val
elif action == 'del':
del self.session[Key]
# 獲取所有信息
Info = self.session.GetAll()
# 返回給前端渲染
self.render("template/index.html", Data=Info)
settings = {
"tempalte_path": "template",
"cookie_secret": "508CE6152CB93994628D3E99934B83CC",
}
application = tornado.web.Application([
(r'/', MainHandler),
], **settings)
if __name__ == "__main__":
application.listen(9999)
tornado.ioloop.IOLoop.instance().start()template\index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
</head>
<body>
<form action="/" method="post">
set/del:<input type="text" name="action" value="set"/>
Key: <input type="text" name="key"/>
Val: <input type="text" name="val"/>
<input type="submit" value="設置"/>
</form>
{{ Data }}
</body>
</html>RedisToSession.py
# _*_ coding: utf-8 _*_
import redis
import hashlib
import uuid
import json
# 連接memcached
pool = redis.ConnectionPool(host='192.168.56.100', port=6379)
conn = redis.Redis(connection_pool=pool)
class Session:
CookieID = 'uc'
ExpiresTime = 60 * 20
def __init__(self, handler):
"""
用於創建用戶session在redis中的字典
:param handler: 請求頭
"""
self.handler = handler
# 從客戶端獲取隨機字符串
SessionID = self.handler.get_secure_cookie(Session.CookieID, None)
# 客戶端存在並且在服務端也存在
if SessionID and conn.exists(SessionID):
self.SessionID = SessionID
else:
# 獲取隨機字符串
self.SessionID = self.SessionKey()
# 把隨機字符串寫入memcached,時間是20分鐘
conn.hset(self.SessionID, None, None)
# 每次訪問超時時間就加20分鐘
conn.expire(self.SessionID, Session.ExpiresTime)
# 設置Cookie
self.handler.set_secure_cookie('uc', self.SessionID)
def SessionKey(self):
"""
:return: 生成隨機字符串
"""
UUID = str(uuid.uuid1()).replace('-', '')
MD5 = hashlib.md5()
MD5.update(bytes(UUID, encoding='utf-8'))
SessionKey = MD5.hexdigest()
return SessionKey
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
"""
:param key: session信息中的key
:param value: 對應的Value
"""
conn.hset(self.SessionID, key, value)
def __getitem__(self, item):
"""
:param item: Session信息中對應的Key
:return: 獲取的Session信息
"""
# 獲取對應的數據
ResultData = conn.hget(self.SessionID, item)
return ResultData
def __delitem__(self, key):
"""
:param key: 要刪除的Key
"""
conn.hdel(self.SessionID, key)
def GetAll(self):
# 獲取Session中所有的信息,僅用於測試
SessionData = conn.hgetall(self.SessionID)
return SessionData