今天我會帶大家真正寫一個Django項目,對於入門來說是有點難度的,因爲邏輯比較複雜,但是真正的知識就是函數與面向對象,這也是培養用Django思維寫項目的開始
Django文件配置
Django模版文件配置
文件路徑 test_site -- test_site -- settings.py
TEMPLATES = [
{
'BACKEND': 'django.template.backends.django.DjangoTemplates',
'DIRS': [os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "template")], # template文件夾位置
'APP_DIRS': True,
'OPTIONS': {
'context_processors': [
'django.template.context_processors.debug',
'django.template.context_processors.request',
'django.contrib.auth.context_processors.auth',
'django.contrib.messages.context_processors.messages',
],
},
},
]Django靜態文件配置
文件路徑 test_site -- test_site -- settings.py
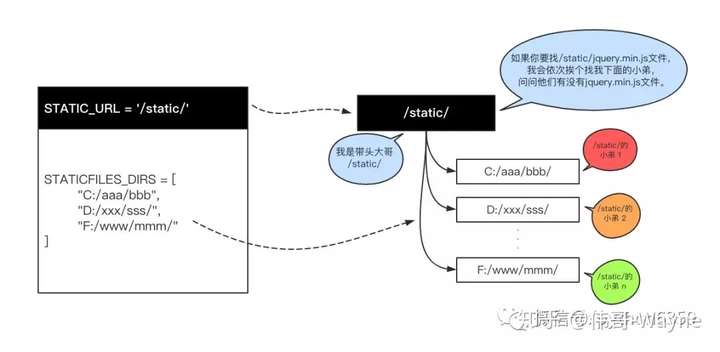
STATIC_URL = '/static/' # HTML中使用的靜態文件夾前綴 STATICFILES_DIRS = [ os.path.join(BASE_DIR, "static"), # 靜態文件存放位置 ]
看不明白?有圖有真相:
剛開始學習時可在配置文件中暫時禁用csrf中間件,方便表單提交測試。
文件路徑 test_site -- test_site -- settings.py
MIDDLEWARE = [ 'django.middleware.security.SecurityMiddleware', 'django.contrib.sessions.middleware.SessionMiddleware', 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware', # 'django.middleware.csrf.CsrfViewMiddleware', 'django.contrib.auth.middleware.AuthenticationMiddleware', 'django.contrib.messages.middleware.MessageMiddleware', 'django.middleware.clickjacking.XFrameOptionsMiddleware', ]
Django 數據庫配置
Django爲什麼要配置數據庫
因爲Django默認採用的是sqlite3數據庫,而我們用Pycharm編寫程序時使用的是Pymysql模塊和數據庫交互的,爲了能夠簡化編寫程序的流程,我們需要修改默認數據庫配置
在修改數據配置之前,我們是不是要先有數據庫,請先創建一個MySQL數據庫吧
文件路徑 test_site -- test_site -- settings.py
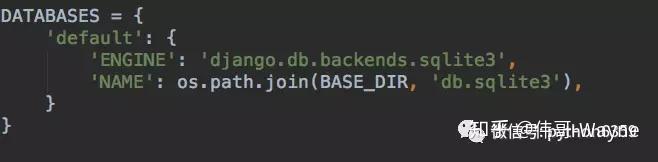
DATABASES = {
'default': {
'ENGINE': 'django.db.backends.mysql', # 注意這幾個用大寫的單詞,必須寫大寫,這些坑我都走過,也浪費了不少時間,希望你不要再走
'NAME': 'test_site',
'HOST': '127.0.0.1',
'PORT': 3306,
'USER': 'root',
'PASSWORD': '', # 我的數據庫是沒有密碼的,你的密碼是什麼就寫什麼,沒有就留空
}
}在和settings.py同目錄下的 __init__.py文件中做配置
文件路徑 test_site -- test_site -- __init__.py
import pymysql pymysql.install_as_MySQLdb()
至此,用Django寫項目,相關的配置已完成,但是有一些關於Django的基礎知識要學習,就像print一樣簡單,這也是我們寫項目的準備工作之一
Django基礎必備三件套(三個小模塊)
HttpResponse 把數據返回給瀏覽器
這個模塊名字起的特別好,根據名字就能大概猜出來的他的意思,真會起名字,不想某些人,寫一套編程語言,用個什麼蟒蛇,寫個框架用個樂手的名字,真的是不爲程序員着想
內部傳入一個字符串,返回給瀏覽器,我們在上一章的Hello World就是這麼寫的
def index(request):
# 業務邏輯代碼
return HttpResponse("Hello World")render 對位填充
render 本意就是着色,粉刷的意思,很好理解,使用方式需要記住
除request參數外還接受一個待渲染的模板文件和一個保存具體數據的字典參數。
將數據填充進模板文件,最後把結果返回給瀏覽器。(類似於我們上章用到的jinja2)
def index(request):
# 業務邏輯代碼
return render(request, "index.html", {"name": "Albert", "hobby": ["音樂", "籃球"]})redirect 重定向
接受一個URL參數,表示跳轉到指定的URL
注意:“” 裏面的兩個/ / 能少,不寫會報錯!注意:“” 裏面的兩個/ / 能少,不寫會報錯!注意:“” 裏面的兩個/ / 能少,不寫會報錯!
def index(request):
# 業務邏輯代碼
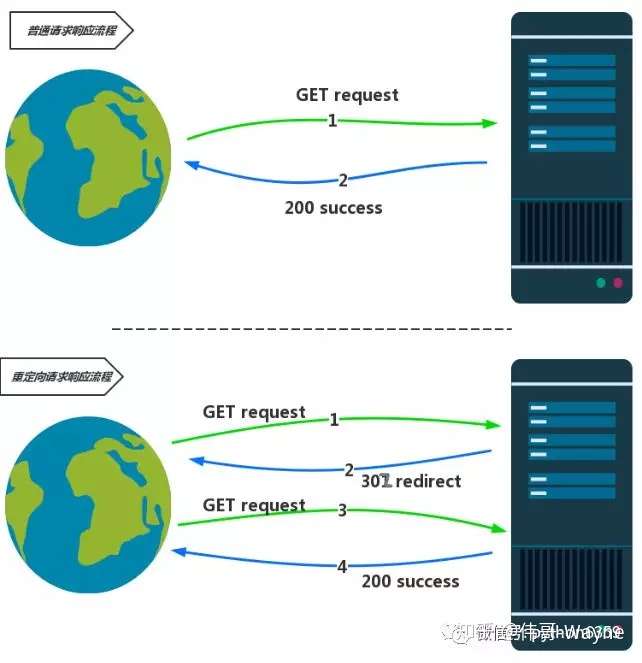
return redirect("/home/")重定向實現原理
redirect 默認的302(臨時重定向),30* 都是重定向,301是永久重定向,對於seo工程師用永久重定向比較多,如果要變爲永久重定向,只需要
在redirect()裏面增加這段代碼即可
permanent=True
Django寫圖書管理系統
目標要求:
分別展示出出版社頁面,書籍頁面和作者頁面
一個出版社可以出版多本書籍(一對多)
一個作者可以寫多本書,一本書也可有多個作者(多對多)
在完成以上配置之後,其實這個程序就已經寫了一半了,是Django幫你寫的,接下來真正的Python代碼我們只需要寫函數和類,在實際的工作中,也是這樣的
爲了能讓大家更清楚掌握用Django寫程序的過程,接下來我們按照過程先後帶領大家把這個程序實現
創建Django項目
開始項目
在終端下寫入如下指令
# Django-admin startproject lms# cd lms# python3 manage.py startapp app01
當然以上操作你也可以在Pycharm上進行,完全沒有問題
創建數據庫
注意數據庫的名字,自己創建
修改配置
按照以上方法操作執行
建立url對應關係
在用戶通過鏈接訪問你的網站的時候,對於用戶來說這是一個鏈接地址,對於程序來時其實是一個函數,通過這個函數才找到數據庫中的對象,對象的方法和整個的前端頁面
文件路徑:和settings同目錄下
"""lms URL Configuration
The `urlpatterns` list routes URLs to views. For more information please see:
https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/1.11/topics/http/urls/
Examples:
Function views
1. Add an import: from my_app import views
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', views.home, name='home')
Class-based views
1. Add an import: from other_app.views import Home
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^$', Home.as_view(), name='home')
Including another URLconf
1. Import the include() function: from django.conf.urls import url, include
2. Add a URL to urlpatterns: url(r'^blog/', include('blog.urls'))
"""
from django.conf.urls import url
from django.contrib import admin
from app01 import views
urlpatterns = [
# 管理員賬戶登陸
url(r'^admin/', admin.site.urls),
# 出版社列表
url(r'^publisher_list/', views.publisher_list),
# 添加出版社
url(r'^add_publisher/', views.add_publisher),
# 刪除出版社
url(r'^drop_publisher/', views.drop_publisher),
# 修改出版社
url(r'^edit_publisher/', views.edit_publisher),
url(r'^book_list/', views.book_list),
url(r'^add_book/', views.add_book),
url(r'^drop_book/', views.drop_book),
url(r'^edit_book/', views.edit_book),
url(r'^author_list/', views.author_list),
url(r'^add_author/', views.add_author),
url(r'^drop_author/', views.drop_author),
url(r'^edit_author/', views.edit_author),
url(r'^$', views.publisher_list), # 只有跟網址,默認匹配
]開始寫Django項目
創建對象,並關聯數據庫
找到app01這個文件夾,也就是項目應用的主文件夾下面有modes.py 文件,這個文件就是我們用來存放類和對象的文件,這裏需要用到ORM(對象關係映射),這裏我們先記住他的使用方法就好了,過幾天帶大家手寫一個ORM。
注意:其他文件不要動,其他文件不要動,其他文件不要動
from django.db import models # Create your models here. # 出版社類 class Publisher(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) name = models.CharField(max_length=64) # 書籍的類 class Book(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) name = models.CharField(max_length=64) publisher = models.ForeignKey(to=Publisher) # Django中創建外鍵聯表操作 # 作者的類 class Author(models.Model): id = models.AutoField(primary_key=True) name = models.CharField(max_length=64) # 一個作者可以對應多本書,一本書也可以有多個作者,多對多,在數據庫中創建第三張表 book = models.ManyToManyField(to=Book)
寫核心邏輯函數
同樣是app01文件夾下的views.py這個文件,上面的urls.py文件中的函數都是從這個文件中引入的,這個文件是最主要的文件
from django.shortcuts import render, redirect
# Create your views here.
from app01 import models
# 出版社列表
def publisher_list(request):
# 查詢
publisher = models.Publisher.objects.all() # ORM中的查詢全部
# 渲染
return render(request, 'publisher_list.html', {'publisher_list': publisher})
# 添加出版社
def add_publisher(request):
# POST請求表示用戶已提交數據
if request.method == 'POST':
new_publisher_name = request.POST.get('name')
models.Publisher.objects.create(name=new_publisher_name)
return redirect('/publisher_list/')
# 渲染待添加頁面給用戶
return render(request, 'add_publisher.html')
# 刪除出版社
def drop_publisher(request):
# GET請求拿到url中的ID
drop_id = request.GET.get('id')
drop_obj = models.Publisher.objects.get(id=drop_id)
drop_obj.delete()
return redirect('/publisher_list/')
# 編輯出版社
def edit_publisher(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Publisher.objects.get(id=edit_id)
new_name = request.POST.get('name')
edit_obj.name = new_name
# 注意保存
edit_obj.save()
return redirect('/publisher_list/')
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Publisher.objects.get(id=edit_id)
return render(request, 'edit_publisher.html', {'publisher': edit_obj})
# 書籍的列表
def book_list(request):
book = models.Book.objects.all()
return render(request, 'book_list.html', {'book_list': book})
# 添加本書籍
def add_book(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
new_book_name = request.POST.get('name')
publisher_id = request.POST.get('publisher_id')
models.Book.objects.create(name=new_book_name, publisher_id=publisher_id)
return redirect('/book_list/')
res = models.Publisher.objects.all()
return render(request, 'add_book.html', {'publisher_list': res})
# 刪除本書籍
def drop_book(request):
drop_id = request.GET.get('id')
drop_obj = models.Book.objects.get(id=drop_id)
drop_obj.delete()
return redirect('/book_list/')
# 編輯本書籍
def edit_book(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
new_book_name = request.POST.get('name')
new_publisher_id = request.POST.get('publisher_id')
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Book.objects.get(id=edit_id)
edit_obj.name = new_book_name
edit_obj.publisher_id = new_publisher_id
edit_obj.save()
return redirect('/book_list/')
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Book.objects.get(id=edit_id)
all_publisher = models.Publisher.objects.all()
return render(request, 'edit_book.html', {'book': edit_obj, 'publisher_list': all_publisher})
# 作者的列表
def author_list(request):
author = models.Author.objects.all()
return render(request, 'author_list.html', {'author_list': author})
# 添加個作者
def add_author(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
new_author_name = request.POST.get('name')
models.Author.objects.create(name=new_author_name)
return redirect('/author_list/')
return render(request, 'add_author.html')
# 刪除個作者
def drop_author(request):
drop_id = request.GET.get('id')
drop_obj = models.Author.objects.get(id=drop_id)
drop_obj.delete()
return redirect('/author_list/')
# 修改下作者
def edit_author(request):
if request.method == 'POST':
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Author.objects.get(id=edit_id)
new_author_name = request.POST.get('name')
new_book_id = request.POST.getlist('book_id')
edit_obj.name = new_author_name
edit_obj.book.set(new_book_id)
edit_obj.save()
return redirect('/author_list/')
edit_id = request.GET.get('id')
edit_obj = models.Author.objects.get(id=edit_id)
all_book = models.Book.objects.all()
return render(request, 'edit_author.html', {
'author': edit_obj,
'book_list': all_book
})寫前端頁面
前端基本上是一直在重複的頁面,注意幾個與後端建立聯繫的地方就好了
<tbody>
{% for publisher in publisher_list %}
<tr>
<td>{{ forloop.counter }}</td>
<td>{{ publisher.name }}</td>
<td class="text-center">
<a class="btn btn-info btn-sm" href="/edit_publisher/?id={{ publisher.id }}"><i
class="fa fa-pencil fa-fw"
aria-hidden="true"></i>編輯
</a>
<a class="btn btn-danger btn-sm" href="/drop_publisher/?id={{ publisher.id }}"><i
class="fa fa-trash-o fa-fw"
aria-hidden="true"></i>刪除
</a>
</td>
</tr>
{% endfor %}
</tbody>前端複雜的部分是與數據庫多表查詢的部分,需要用for循環,注意for循環在Django中的使用方式
<select class="form-control" name="publisher_id">
{% for publisher in publisher_list %}
{# 如果當前循環到的出版社 和 書關聯的出版社 相等 #}
{% if publisher == book.publisher %}
<option selected
value="{{ publisher.id }}">{{ publisher.name }}</option>
{% else %}
<option value="{{ publisher.id }}">{{ publisher.name }}</option>
{% endif %}
{% endfor %}
</select>完整代碼已上傳到GIthub,請點擊我的github:https://github.com/mayite/lms訪問下載
文章出處: