HashMap 簡介
HashMap 主要用來存放鍵值對,它基於哈希表的Map接口實現,是常用的Java集合之一。
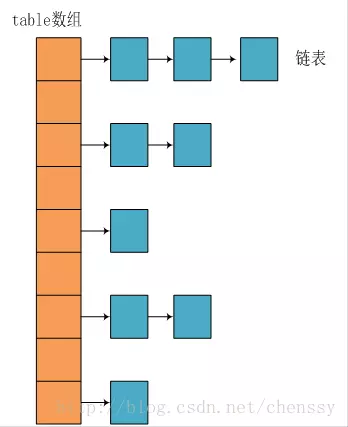
JDK1.8 之前 HashMap 由 數組+鏈表 組成的,數組是 HashMap 的主體,鏈表則是主要爲了解決哈希衝突而存在的(“拉鍊法”解決衝突).JDK1.8 以後在解決哈希衝突時有了較大的變化,當鏈表長度大於閾值(默認爲 8)時,將鏈表轉化爲紅黑樹,以減少搜索時間。
底層數據結構分析
JDK1.8之前
JDK1.8 之前 HashMap 底層是 數組和鏈表 結合在一起使用也就是 鏈表散列。HashMap 通過 key 的 hashCode 經過擾動函數處理過後得到 hash 值,然後通過 (n - 1) & hash 判斷當前元素存放的位置(這裏的 n 指的是數組的長度),如果當前位置存在元素的話,就判斷該元素與要存入的元素的 hash 值以及 key 是否相同,如果相同的話,直接覆蓋,不相同就通過拉鍊法解決衝突。
所謂擾動函數指的就是 HashMap 的 hash 方法。使用 hash 方法也就是擾動函數是爲了防止一些實現比較差的 hashCode() 方法 換句話說使用擾動函數之後可以減少碰撞。
JDK 1.8 HashMap 的 hash 方法源碼:
JDK 1.8 的 hash方法 相比於 JDK 1.7 hash 方法更加簡化,但是原理不變。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
|
對比一下 JDK1.7的 HashMap 的 hash 方法源碼.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
|
相比於 JDK1.8 的 hash 方法 ,JDK 1.7 的 hash 方法的性能會稍差一點點,因爲畢竟擾動了 4 次。
所謂 “拉鍊法” 就是:將鏈表和數組相結合。也就是說創建一個鏈表數組,數組中每一格就是一個鏈表。若遇到哈希衝突,則將衝突的值加到鏈表中即可。
JDK1.8之後
相比於之前的版本,jdk1.8在解決哈希衝突時有了較大的變化,當鏈表長度大於閾值(默認爲8)時,將鏈表轉化爲紅黑樹,以減少搜索時間。
類的屬性:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
loadFactor加載因子
loadFactor加載因子是控制數組存放數據的疏密程度,loadFactor越趨近於1,那麼 數組中存放的數據(entry)也就越多,也就越密,也就是會讓鏈表的長度增加,load Factor越小,也就是趨近於0,
loadFactor太大導致查找元素效率低,太小導致數組的利用率低,存放的數據會很分散。loadFactor的默認值爲0.75f是官方給出的一個比較好的臨界值。
threshold
threshold = capacity * loadFactor,當Size>=threshold的時候,那麼就要考慮對數組的擴增了,也就是說,這個的意思就是 衡量數組是否需要擴增的一個標準。
Node節點類源碼:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 |
|
樹節點類源碼:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 |
|
HashMap源碼分析
構造方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 |
|
putMapEntries方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 |
|
put方法
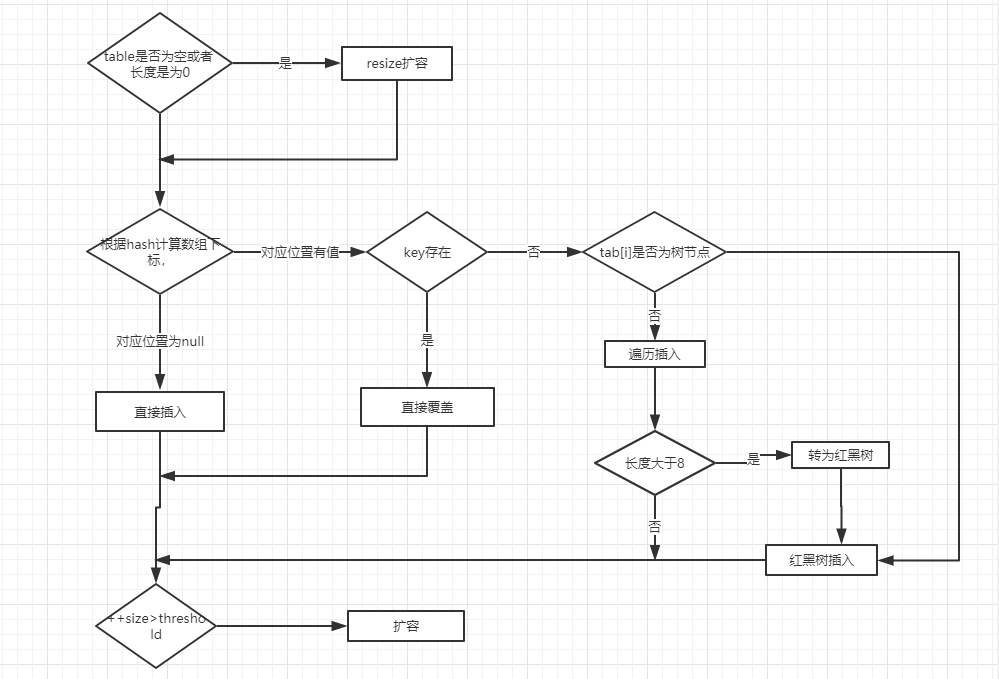
HashMap只提供了put用於添加元素,putVal方法只是給put方法調用的一個方法,並沒有提供給用戶使用。
對putVal方法添加元素的分析如下:
①如果定位到的數組位置沒有元素 就直接插入。
②如果定位到的數組位置有元素就和要插入的 key 比較,如果key相同就直接覆蓋,如果 key 不相同,就判斷 p 是否是一個樹節點,如果是就調用
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value)將元素添加進入。如果不是就遍歷鏈表插入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 |
|
我們再來對比一下 JDK1.7 put方法的代碼
對於put方法的分析如下:
①如果定位到的數組位置沒有元素 就直接插入。
②如果定位到的數組位置有元素,遍歷以這個元素爲頭結點的鏈表,依次和插入的key比較,如果key相同就直接覆蓋,不同就採用頭插法插入元素。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 |
|
get方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 |
|
resize方法
進行擴容,會伴隨着一次重新hash分配,並且會遍歷hash表中所有的元素,是非常耗時的。在編寫程序中,要儘量避免resize。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 |
|
HashMap常用方法測試
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 |
|