Ftrace簡介
Ftrace是Linux進行代碼級實踐分析最有效的工具之一,比如我們進行一個系統調用,出來的時間過長,我們想知道時間花哪裏去了,利用Ftrace就可以追蹤到一級級的時間分佈。
Ftrace案例
寫一個proc模塊,包含一個proc的讀和寫的入口。test_proc_show()故意調用了一個kill_time()的函數,而kill_time()的函數,又調用了mdelay(2)和kill_moretime()的函數,該函數體內調用mdelay(2)。
kill_time()的函數和kill_moretime()函數前面都加了noinline以避免被編譯器inline優化掉。
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/seq_file.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/uaccess.h>
static unsigned int variable;
static struct proc_dir_entry *test_dir, *test_entry;
static noinline void kill_moretime(void)
{
mdelay(2);
}
static noinline void kill_time(void)
{
mdelay(2);
kill_moretime();
}
static int test_proc_show(struct seq_file *seq, void *v)
{
unsigned int *ptr_var = seq->private;
kill_time();
seq_printf(seq, "%u\n", *ptr_var);
return 0;
}
static ssize_t test_proc_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
...
}
static int test_proc_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return single_open(file, test_proc_show, PDE_DATA(inode));
}
static const struct file_operations test_proc_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = test_proc_open,
.read = seq_read,
.write = test_proc_write,
.llseek = seq_lseek,
.release = single_release,
};
static __init int test_proc_init(void)
{
test_dir = proc_mkdir("test_dir", NULL);
if (test_dir) {
test_entry = proc_create_data("test_rw",0666, test_dir, &test_proc_fops, &variable);
if (test_entry)
return 0;
}
return -ENOMEM;
}
module_init(test_proc_init);
static __exit void test_proc_cleanup(void)
{
remove_proc_entry("test_rw", test_dir);
remove_proc_entry("test_dir", NULL);
}
module_exit(test_proc_cleanup);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Barry Song <[email protected]>");
MODULE_DESCRIPTION("proc exmaple");
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");KVERS = $(shell uname -r)
# Kernel modules
obj-m += proc.o
# Specify flags for the module compilation.
#EXTRA_CFLAGS=-g -O0
build: kernel_modules
kernel_modules:
make -C /lib/modules/$(KVERS)/build M=$(CURDIR) modules
clean:
make -C /lib/modules/$(KVERS)/build M=$(CURDIR) clean$ make
baohua@baohua-perf:~/develop/training/debug/ftrace/proc$
$ sudo insmod proc.ko
[sudo] password for baohua:
之後/proc目錄下/proc/test_dir/test_rw文件可被讀寫。
下面我們用Ftrace來跟蹤test_proc_show()這個函數。
我們把啓動ftrace的所有命令寫到一個腳本function.sh裏面:
#!/bin/bash
debugfs=/sys/kernel/debug
echo nop > $debugfs/tracing/current_tracer
echo 0 > $debugfs/tracing/tracing_on
echo $$ > $debugfs/tracing/set_ftrace_pid
echo function_graph > $debugfs/tracing/current_tracer
#replace test_proc_show by your function name
echo test_proc_show > $debugfs/tracing/set_graph_function
echo 1 > $debugfs/tracing/tracing_on
exec "$@"# ./function.sh cat /proc/test_dir/test_rw
0
讀取trace的結果:
# cat /sys/kernel/debug/tracing/trace > 1
接着用vim打開這個文件1,發現這個文件有600多行:
天了擼,長到看不清!!
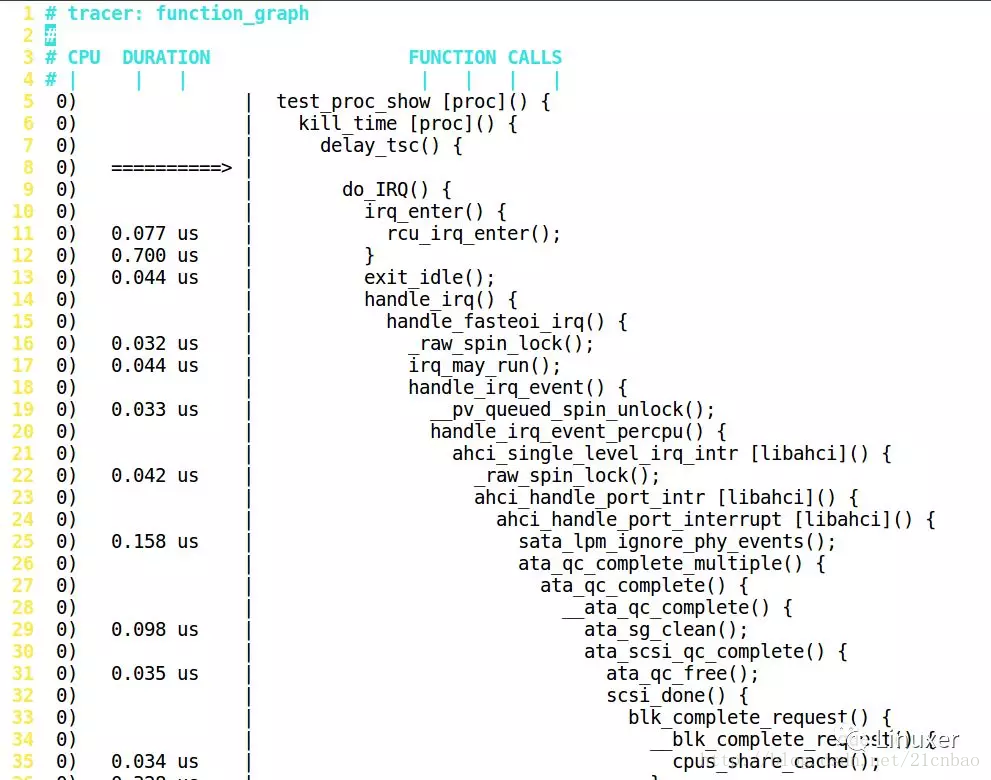
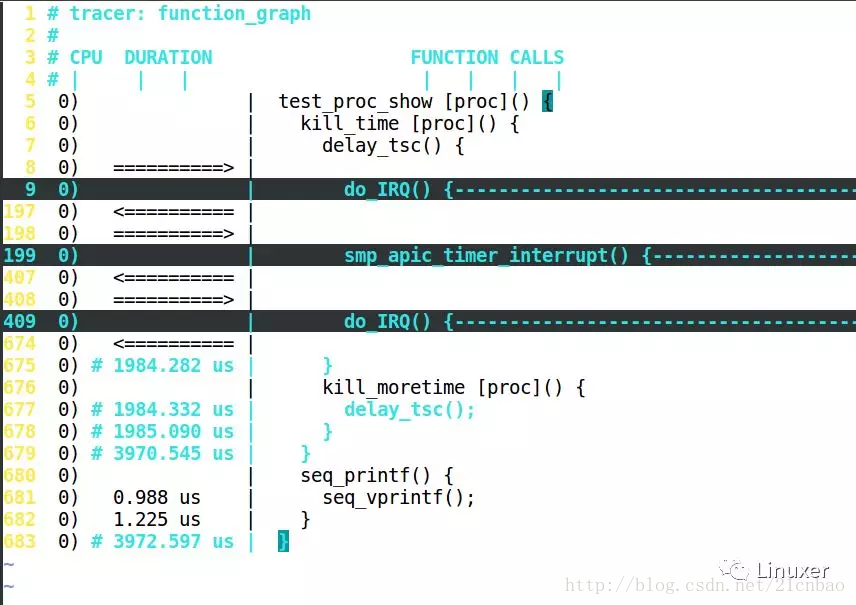
Ftrace結果怎麼讀?
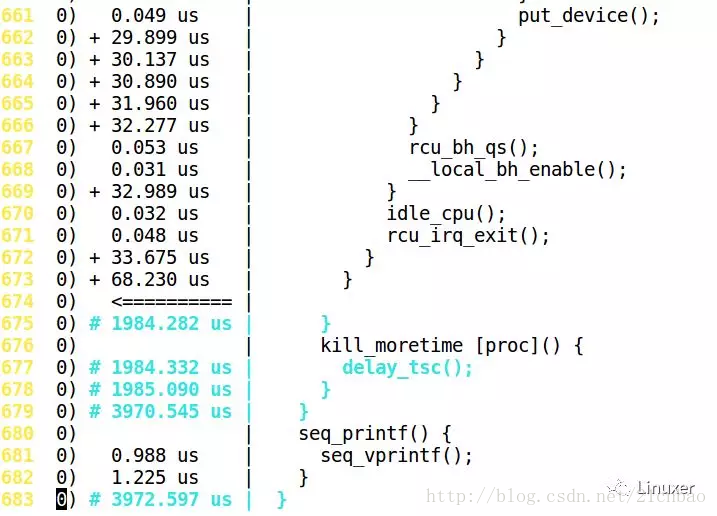
Ftrace結果怎麼讀?答案非常簡單:如果是葉子函數,就直接在這個函數的前面顯示它佔用的時間,如果是非葉子,要等到 }的時候,再顯示時間,如下圖:
延遲比較大的部分,會有+、#等特殊標號:
'$' - greater than 1 second
'@' - greater than 100 milisecond
'*' - greater than 10 milisecond
'#' - greater than 1000 microsecond
'!' - greater than 100 microsecond
'+' - greater than 10 microsecond
' ' - less than or equal to 10 microsecond.
vim對Ftrace進行摺疊
上面那個Ftrace文件太大了,大到看不清。我們可以用vim來摺疊之,不過需要一個vim的特別配置,我把它存放在了我的~目錄,名字叫.fungraph-vim:
" Enable folding for ftrace function_graph traces.
"
" To use, :source this file while viewing a function_graph trace, or use vim's
" -S option to load from the command-line together with a trace. You can then
" use the usual vim fold commands, such as "za", to open and close nested
" functions. While closed, a fold will show the total time taken for a call,
" as would normally appear on the line with the closing brace. Folded
" functions will not include finish_task_switch(), so folding should remain
" relatively sane even through a context switch.
"
" Note that this will almost certainly only work well with a
" single-CPU trace (e.g. trace-cmd report --cpu 1).
function! FunctionGraphFoldExpr(lnum)
let line = getline(a:lnum)
if line[-1:] == '{'
if line =~ 'finish_task_switch() {$'
return '>1'
endif
return 'a1'
elseif line[-1:] == '}'
return 's1'
else
return '='
endif
endfunction
function! FunctionGraphFoldText()
let s = split(getline(v:foldstart), '|', 1)
if getline(v:foldend+1) =~ 'finish_task_switch() {$'
let s[2] = ' task switch '
else
let e = split(getline(v:foldend), '|', 1)
let s[2] = e[2]
endif
return join(s, '|')
endfunction
setlocal foldexpr=FunctionGraphFoldExpr(v:lnum)
setlocal foldtext=FunctionGraphFoldText()
setlocal foldcolumn=12
setlocal foldmethod=expr
之後我們配置vim爲這個模板來打開前面那個600多行的文件1:
vim -S ~/.fungraph-vim 1
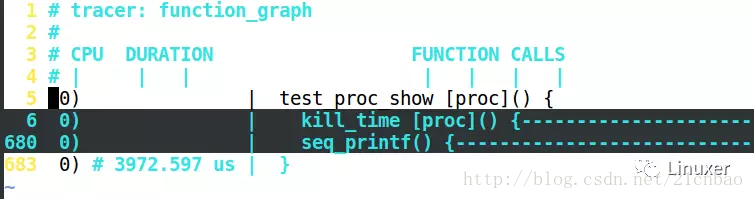
這樣我們看到的樣子是:
我們可以把光標移動到第5行,鍵盤敲打za,則展開爲:
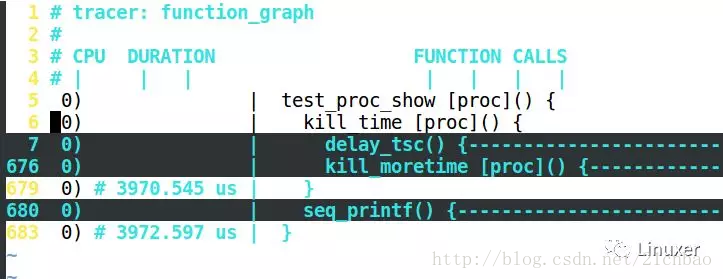
繼續展開第6行的kill_time(),按za:
我們可以用z、a兩個按鍵,搜索或者展開Ftrace的結果。
最後,https://github.com/brendangregg/perf-tools對Ftrace的功能進行了很好的封裝和集成,建議大家用perf-tools來使用Ftrace,則效果更佳更簡單。
有空再聊perf-tools。