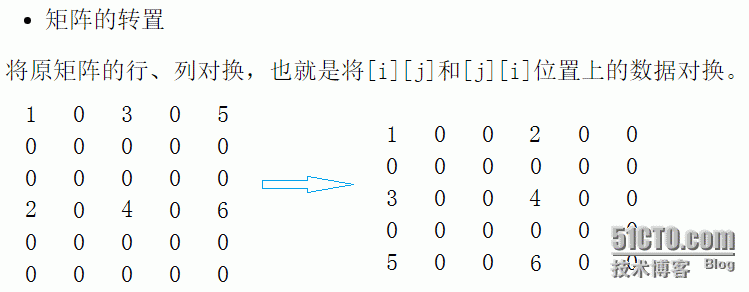
稀疏矩阵是矩阵中非零元素的个数远远小于矩阵元素的总数,并且非零元素的分布没有规律,通常认为非零元素比上矩阵所有元素的值小于等于0.05时,则称该矩阵为稀疏矩阵(sparse matrix);与之相区别的是,如果非零元素的分布存在规律(如上三角矩阵、下三角矩阵、对角矩阵),则称该矩阵为特殊矩阵。
一个稀疏矩阵中有许多元素等于零,这便于矩阵的计算和保存.如果Matlab把一个矩阵当作稀疏矩阵,那么只需在m×3的矩阵中存储m个非零项.第1列是行下标,第2列是列下标,第3列是非零元素值,不必保存零元素.如果存储一个浮点数要8个字节,存储每个下标要4个字节,那么整个矩阵在内存中存储需要1 6×m个字节.
A = e y e ( 1 0 0 0 ) ;
得到一个1 0 0 0×1 0 0 0的单位矩阵,存储它需要8 MB空间.如果使用命令:
B = s p e y e ( 1 0 0 0 ) ;
用一个1 0 0 0×3的矩阵来代表,每行包含有一个行下标,列下标和元素本身.只需1 6 K B的空间就可以存储1 0 0 0×1 0 0 0的单位矩阵,它只需要满单位矩阵的0 . 2 %存储空间.对于许多的广义矩阵也可这样来作.
对于存稀疏矩阵我们首先定义一个三元组,压缩存储值存储极少数的有效数据。使用{row,col,value}三元组存储每一个有效数据,三元组按原矩阵中的位置,以行优先级先后顺序依次存放。
struct Triple
{
int _row; //行
int _col; //列
T _value; //值
Triple(int row, int col, T& value)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
,_value(value)
{}
Triple()
:_row(0)
, _col(0)
, _value(0)
{}
};普通转置:
SparseMatrix(T* a, int m, int n, const T& invalid)//非法值
:_rowsize(m)
,_colsize(n)
,_invaild(invalid)
{
for (int i=0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[i*n + j] != invalid)
{
Triple<T> tmp(i, j, a[i*n + j]);
_a.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
}
SparseMatrix()
{}
SparseMatrix(size_t rowsize, size_t colsize, T invaild)
:_rowsize(rowsize),
_colsize(colsize),
_invaild(invaild)
{}
// 转置
SparseMatrix<T> Transport()
{ //务必保持行优先
SparseMatrix<T> sm(_colsize, _rowsize, _invaild);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _colsize; i++)
{
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
if (_a[index]._col == i)
{
Triple<T> mm;
mm._col = _a[index]._row;
mm._row = _a[index]._col;
mm._value = _a[index]._value;
sm._a.push_back(mm);
}
++index;
}
}
return sm;
}SparseMatrix<T> FastTransport() //快速转置
{
SparseMatrix<T> temp;
temp._a.resize(_a.size());
int* rowcounts = new int[_col];
int* rowstarts = new int[_col];
memset(rowcounts, 0, sizeof((int)*_col));
memset(rowstarts, 0, sizeof((int)*_col));
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
rowcounts[_a[index]._col]++;
++index;
}
rowstarts[0] = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _col; ++i)
{
rowstarts[i] = rowstarts[i - 1] + rowcounts[i - 1];
}
while (index < _a.size())
{
size_t& begin = rowstarts[_a[index]._col];
Triple<T> tp;
tp._row = _a[index]._col;
tp._col = _a[index]._row;
tp._value = _a[index]._value;
tmp._a[rowstarts++] = tp;
++index;
}
delete[] _a;
return tmp;
}打印矩阵部分实现:
void display(T* a, int m, int n, const T& invalid)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (p < _a.size() && _a[p]._row == i&&_a[p]._col == j)
{
cout << _a[p]._value << " ";
p++;
}
else
{
cout << invalid << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}完整实现代码:
#pragma once
#include<vector>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
struct Triple
{
int _row;
int _col;
T _value;
Triple(int row, int col, T& value)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
,_value(value)
{}
Triple()
:_row(0)
, _col(0)
, _value(0)
{}
};
template<class T>
class SparseMatrix
{
public:
SparseMatrix(T* a, int m, int n, const T& invalid)//非法值
:_rowsize(m)
,_colsize(n)
,_invaild(invalid)
{
for (int i=0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (a[i*n + j] != invalid)
{
Triple<T> tmp(i, j, a[i*n + j]);
_a.push_back(tmp);
}
}
}
}
SparseMatrix()
{}
SparseMatrix(size_t rowsize, size_t colsize, T invaild)
:_rowsize(rowsize),
_colsize(colsize),
_invaild(invaild)
{}
void display(T* a, int m, int n, const T& invalid)
{
int p = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < m; ++i)
{
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
{
if (p < _a.size() && _a[p]._row == i&&_a[p]._col == j)
{
cout << _a[p]._value << " ";
p++;
}
else
{
cout << invalid << " ";
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}
SparseMatrix<T> Transport()
{ //务必保持行优先
SparseMatrix<T> sm(_colsize, _rowsize, _invaild);
for (size_t i = 0; i < _colsize; i++)
{
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
if (_a[index]._col == i)
{
Triple<T> mm;
mm._col = _a[index]._row;
mm._row = _a[index]._col;
mm._value = _a[index]._value;
sm._a.push_back(mm);
}
++index;
}
}
return sm;
}
SparseMatrix<T> FastTransport() //快速转置
{
SparseMatrix<T> temp;
temp._a.resize(_a.size());
int* rowcounts = new int[_col];
int* rowstarts = new int[_col];
memset(rowcounts, 0, sizeof((int)*_col));
memset(rowstarts, 0, sizeof((int)*_col));
size_t index = 0;
while (index < _a.size())
{
rowcounts[_a[index]._col]++;
++index;
}
rowstarts[0] = 0;
for (size_t i = 0; i < _col; ++i)
{
rowstarts[i] = rowstarts[i - 1] + rowcounts[i - 1];
}
while (index < _a.size())
{
size_t& begin = rowstarts[_a[index]._col];
Triple<T> tp;
tp._row = _a[index]._col;
tp._col = _a[index]._row;
tp._value = _a[index]._value;
tmp._a[rowstarts++] = tp;
++index;
}
delete[] _a;
return tmp;
}
protected:
size_t _rowsize;
size_t _colsize;
T _invaild;
vector<Triple<T>> _a;
};
void test()
{
int a[6][5] =
{
{ 1, 0, 3, 0, 5 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 2, 0, 4, 0, 6 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }
};
SparseMatrix<int> d((int*)a,6,5,0);
SparseMatrix<int> tmp=d.Transport();
cout << "转置之前:" << endl;
d.display((int*)a,6,5,0);
cout << endl;
cout << "转置之后:" << endl;
tmp.display((int*)a, 5, 6, 0);
}结果截图

![5Z_(UW]_Q6$VX8`7CKVQLS7.png wKioL1cYWMOzuo7yAABPevHCXtA472.png](http://s5.51cto.com/wyfs02/M02/7F/43/wKioL1cYWMOzuo7yAABPevHCXtA472.png)
