一. 前言
ImageLoader的圖片緩存分成磁盤和內存兩種,這裏分析一下磁盤緩存以及圖片文件名算法的實現
默認是不存儲在磁盤上的,需要手動打開開關
如下
DisplayImageOptions options = new DisplayImageOptions.Builder()
.cacheInMemory(true) // default false
.cacheOnDisk(true) // default false
imageLoader.displayImage("", imageView, options, null, null);二. 磁盤文件命名
/**
* Generates names for files at disk cache
*
* @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
* @since 1.3.1
*/
public interface FileNameGenerator {
/** Generates unique file name for image defined by URI */
String generate(String imageUri);
}接口是FileNameGenerator,此接口非常簡單明瞭,只有一個根據圖片uri產生一個圖片文件名稱的方法。
它包含兩個實現類
- HashCodeFileNameGenerator
- Md5FileNameGenerator
接下來,分別看這兩個類的實現
2.1 HashCodeFileNameGenerator
/**
* Names image file as image URI {@linkplain String#hashCode() hashcode}
*
* @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
* @since 1.3.1
*/
public class HashCodeFileNameGenerator implements FileNameGenerator {
@Override
public String generate(String imageUri) {
return String.valueOf(imageUri.hashCode());
}
}實現比較簡單,根據uri的hashcode轉化成String即可,默認就是Hashcode命名。
2.2 Md5FileNameGenerator
/**
* Names image file as MD5 hash of image URI
*
* @author Sergey Tarasevich (nostra13[at]gmail[dot]com)
* @since 1.4.0
*/
public class Md5FileNameGenerator implements FileNameGenerator {
private static final String HASH_ALGORITHM = "MD5";
private static final int RADIX = 10 + 26; // 10 digits + 26 letters
@Override
public String generate(String imageUri) {
byte[] md5 = getMD5(imageUri.getBytes());
BigInteger bi = new BigInteger(md5).abs();
return bi.toString(RADIX);
}
private byte[] getMD5(byte[] data) {
byte[] hash = null;
try {
MessageDigest digest = MessageDigest.getInstance(HASH_ALGORITHM);
digest.update(data);
hash = digest.digest();
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
L.e(e);
}
return hash;
}
}通過imageUri得到byte數組,然後通過MD5算法得到文件名
三. 磁盤目錄選擇
一般默認優先選擇sdk/android/data/packageName/cache/uil-images卡,如果sdk目錄創建失敗,那麼會選擇/data/data/packageName目錄
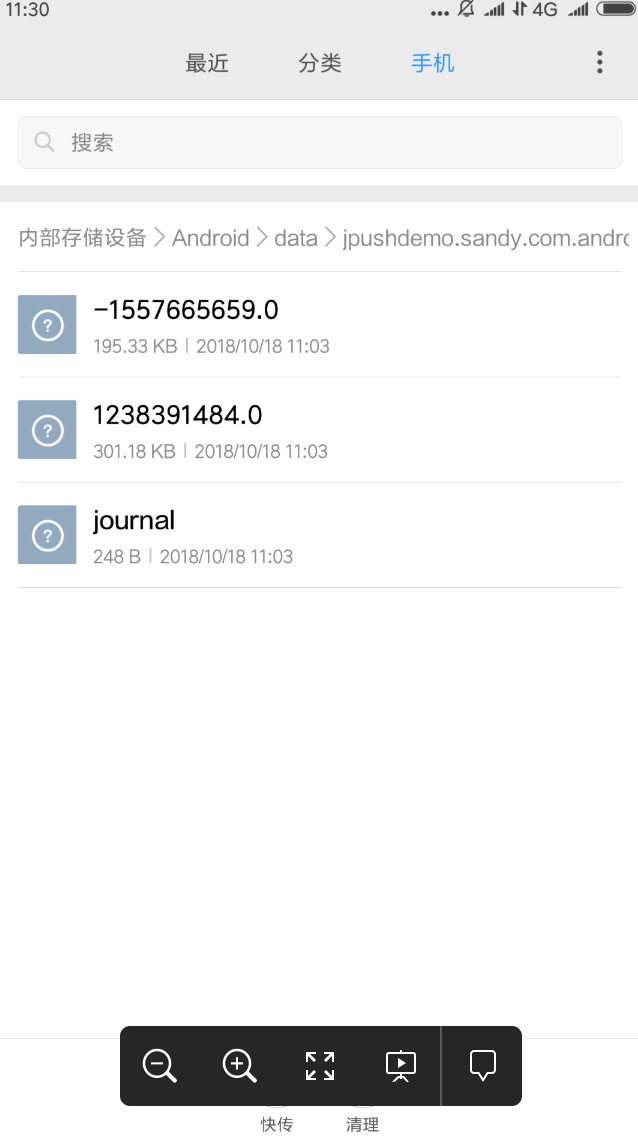
四. 圖片緩存示例
其中-1557665659.0和1238391484.0兩個就是圖片存儲文件
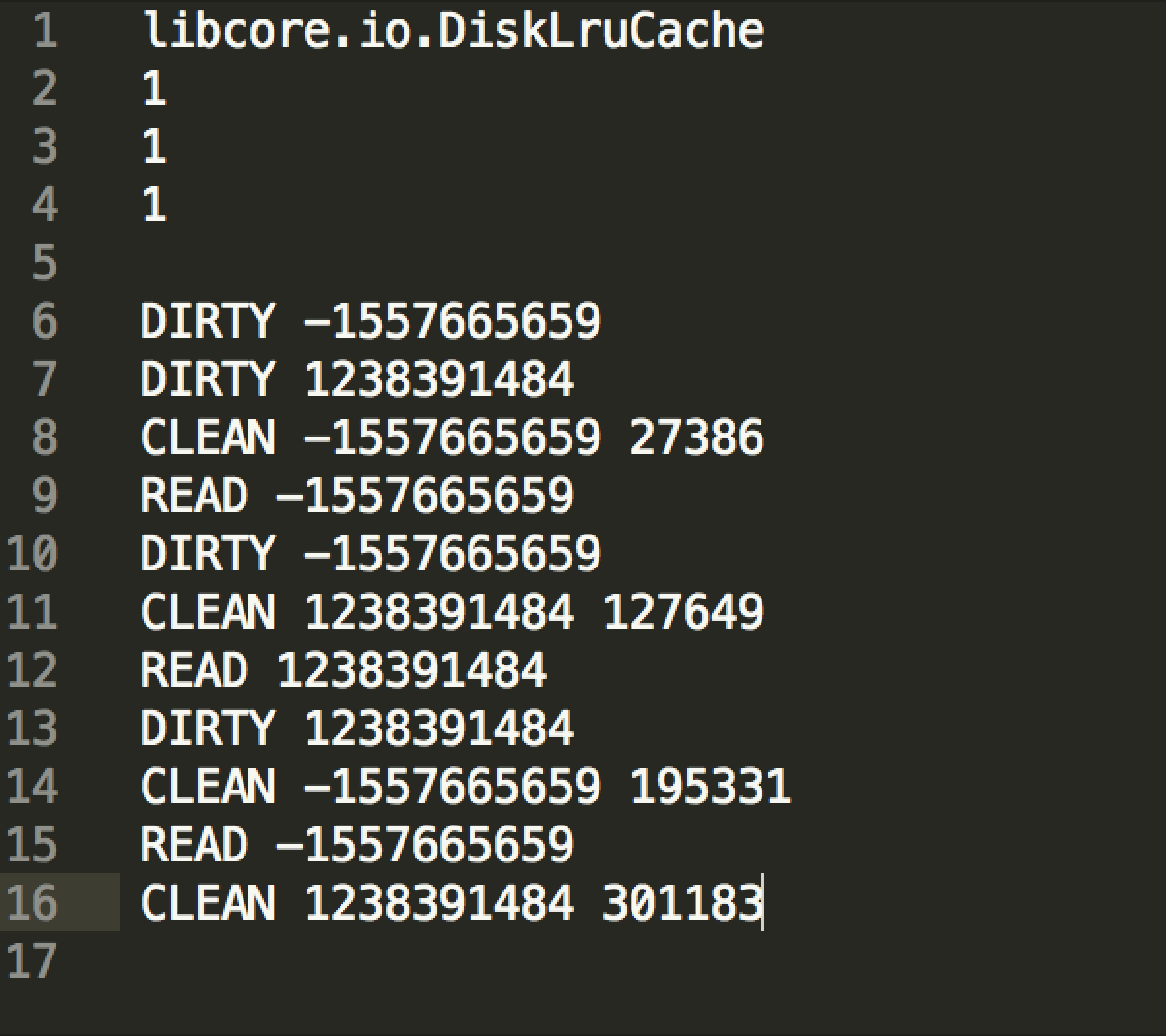
journal是操作記錄描述性文件,內容如下
- DIRTY: 操作記錄創建,如果DIRTY後面沒有CLEAN或者REMOVE,那麼這個圖片會被刪除。
- CLEAN: 記錄成功創建和訪問
- READ: 記錄成功訪問
- REMOVE: 記錄刪除
五. 磁盤緩存接口
磁盤緩存算法的接口是DiskCache,接口很簡單明瞭。
public interface DiskCache {
File getDirectory();
File get(String imageUri);
boolean save(String imageUri, InputStream imageStream, IoUtils.CopyListener listener) throws IOException;
boolean save(String imageUri, Bitmap bitmap) throws IOException;
boolean remove(String imageUri);
void close();
void clear();
}| 方法名 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| getDirectory() | 獲取存儲目錄 |
| get(String imageUri) | 根據imageUri獲取圖片文件 |
| save(String imageUri, InputStream imageStream, IoUtils.CopyListener listener) | 保存圖片 |
| remove(String imageUri) | 刪除圖片緩存 |
| close() | 關閉磁盤緩存,釋放資源 |
| clear() | 清理所有的磁盤緩存 |
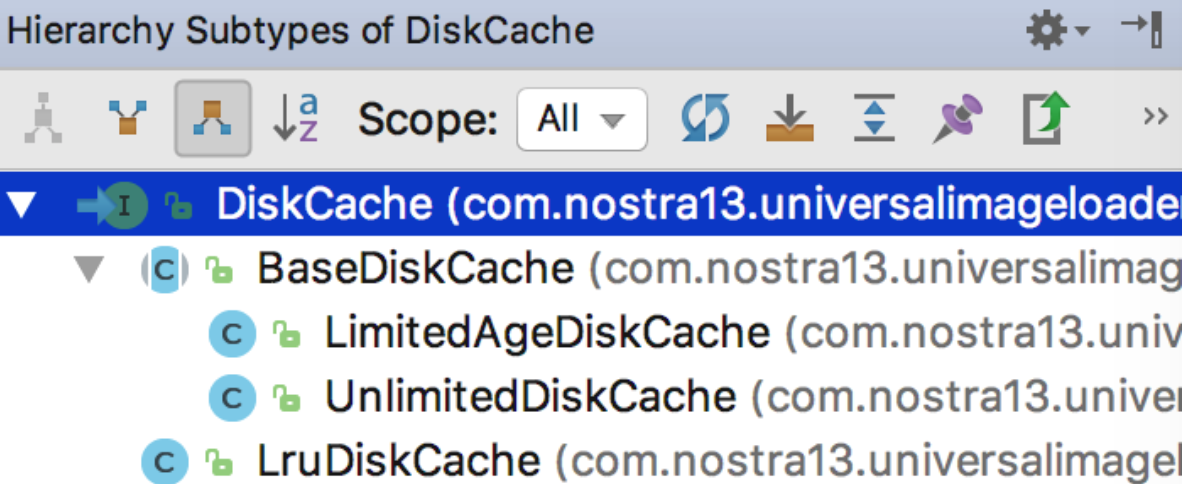
5.1 實現類
下面詳細看每個類的實現
六. LruDiskCache
public class LruDiskCache implements DiskCache {
protected DiskLruCache cache;
...
protected final FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator;
...
public LruDiskCache(File cacheDir, File reserveCacheDir, FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator, long cacheMaxSize,
int cacheMaxFileCount) throws IOException {
...
initCache(cacheDir, reserveCacheDir, cacheMaxSize, cacheMaxFileCount);
}
private void initCache(File cacheDir, File reserveCacheDir, long cacheMaxSize, int cacheMaxFileCount)
throws IOException {
try {
cache = DiskLruCache.open(cacheDir, 1, 1, cacheMaxSize, cacheMaxFileCount);
} catch (IOException e) {
...
}
}
@Override
public File getDirectory() {
return cache.getDirectory();
}
@Override
public File get(String imageUri) {
DiskLruCache.Snapshot snapshot = null;
try {
snapshot = cache.get(getKey(imageUri));
return snapshot == null ? null : snapshot.getFile(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
return null;
} finally {
if (snapshot != null) {
snapshot.close();
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean save(String imageUri, InputStream imageStream, IoUtils.CopyListener listener) throws IOException {
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = cache.edit(getKey(imageUri));
if (editor == null) {
return false;
}
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(editor.newOutputStream(0), bufferSize);
boolean copied = false;
try {
copied = IoUtils.copyStream(imageStream, os, listener, bufferSize);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeSilently(os);
if (copied) {
editor.commit();
} else {
editor.abort();
}
}
return copied;
}
...
@Override
public boolean remove(String imageUri) {
try {
return cache.remove(getKey(imageUri));
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
return false;
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
try {
cache.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
}
cache = null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
try {
cache.delete();
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
}
try {
initCache(cache.getDirectory(), reserveCacheDir, cache.getMaxSize(), cache.getMaxFileCount());
} catch (IOException e) {
L.e(e);
}
}
private String getKey(String imageUri) {
return fileNameGenerator.generate(imageUri);
}
}LruDiskCache有幾個比較重要的屬性,
protected DiskLruCache cache;
protected final FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator;FileNameGenerator就是上面說的文件命名生成器,包括hashcode和md5算法。我們思考下,爲什麼需要FileNameGenerator?
個人以爲網絡上面的uri可能是千奇百怪的,甚至包括特殊字符,那作爲文件名顯然不合適。所以,這個時候來一次hashcode,或者md5轉換,獲取文件名是最好的。
DiskLruCache,竊以爲這個命名不是很好,因爲跟LruDiskCache很類似(我第一眼就看成一個東西了!)
這個DiskLruCache很重要,它維護了磁盤圖片文件緩存的操作記錄,緩存和文件對應關係等。
而且如果你仔細看LruDiskCache的各個方法時會發現,基本都是調用cache的對應方法。
所以,我們主要接下來看DiskLruCache代碼
final class DiskLruCache implements Closeable {
...
private final File directory;
private final File journalFile;
...
private Writer journalWriter;
private final LinkedHashMap<String, Entry> lruEntries =
new LinkedHashMap<String, Entry>(0, 0.75f, true);
...
}DiskLruCache包含了journalFile,文件裏面具體的含義可以第四點的樣例。包含了
LinkedHashMap<String, Entry> lruEntries 表示每個圖片的緩存記錄,String表示key, Entry表示圖片的描述信息
private final class Entry {
private final String key;
/** Lengths of this entry's files. */
private final long[] lengths;
/** True if this entry has ever been published. */
private boolean readable;
/** The ongoing edit or null if this entry is not being edited. */
private Editor currentEditor;
/** The sequence number of the most recently committed edit to this entry. */
private long sequenceNumber;
public File getCleanFile(int i) {
return new File(directory, key + "." + i);
}
public File getDirtyFile(int i) {
return new File(directory, key + "." + i + ".tmp");
}
}我們以保存圖片緩存爲例,分析下LruDiskCache的工作流程,首先看LruDiskCache的save方法
public boolean save(String imageUri, InputStream imageStream, IoUtils.CopyListener listener) throws IOException {
DiskLruCache.Editor editor = cache.edit(getKey(imageUri));
if (editor == null) {
return false;
}
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(editor.newOutputStream(0), bufferSize);
boolean copied = false;
try {
copied = IoUtils.copyStream(imageStream, os, listener, bufferSize);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeSilently(os);
if (copied) {
editor.commit();
} else {
editor.abort();
}
}
return copied;
}6.1 getkey(imageUri)
首先根據imageUri生成文件名,也就是key,目前我們用的是hashCode
private String getKey(String imageUri) {
return fileNameGenerator.generate(imageUri);
}6.2 cache.edit
private synchronized Editor edit(String key, long expectedSequenceNumber) throws IOException {
checkNotClosed();
validateKey(key);
Entry entry = lruEntries.get(key);
if (expectedSequenceNumber != ANY_SEQUENCE_NUMBER && (entry == null
|| entry.sequenceNumber != expectedSequenceNumber)) {
return null; // Snapshot is stale.
}
if (entry == null) {
entry = new Entry(key);
lruEntries.put(key, entry);
} else if (entry.currentEditor != null) {
return null; // Another edit is in progress.
}
Editor editor = new Editor(entry);
entry.currentEditor = editor;
// Flush the journal before creating files to prevent file leaks.
journalWriter.write(DIRTY + ' ' + key + '\n');
journalWriter.flush();
return editor;
}從lruEntries裏面根據key獲取到對應的圖片Entry對象,如果沒有就新建一個。
然後利用journalWriter寫入一條DIRTY記錄。
6.3 DiskLruCache 打開Dirty圖片文件流
public OutputStream newOutputStream(int index) throws IOException {
synchronized (DiskLruCache.this) {
if (entry.currentEditor != this) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
if (!entry.readable) {
written[index] = true;
}
File dirtyFile = entry.getDirtyFile(index);
FileOutputStream outputStream;
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dirtyFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// Attempt to recreate the cache directory.
directory.mkdirs();
try {
outputStream = new FileOutputStream(dirtyFile);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e2) {
// We are unable to recover. Silently eat the writes.
return NULL_OUTPUT_STREAM;
}
}
return new FaultHidingOutputStream(outputStream);
}
}public File getDirtyFile(int i) {
return new File(directory, key + "." + i + ".tmp");
}注意這裏打開的是drity文件,就是正常的文件後面加上一個.tmp後綴。
6.4 copyStream把網絡圖片流寫入Dirty文件
public static boolean copyStream(InputStream is, OutputStream os, CopyListener listener, int bufferSize)
throws IOException {
int current = 0;
int total = is.available();
if (total <= 0) {
total = DEFAULT_IMAGE_TOTAL_SIZE;
}
final byte[] bytes = new byte[bufferSize];
int count;
if (shouldStopLoading(listener, current, total)) return false;
while ((count = is.read(bytes, 0, bufferSize)) != -1) {
os.write(bytes, 0, count);
current += count;
if (shouldStopLoading(listener, current, total)) return false;
}
os.flush();
return true;
}private static boolean shouldStopLoading(CopyListener listener, int current, int total) {
if (listener != null) {
boolean shouldContinue = listener.onBytesCopied(current, total);
if (!shouldContinue) {
if (100 * current / total < CONTINUE_LOADING_PERCENTAGE) {
return true; // if loaded more than 75% then continue loading anyway
}
}
}
return false;
}很普通的文件流讀寫,有意思的是shouldStopLoading,它給了我們一個使用listener終止copy的時機。
public static interface CopyListener {
/**
* @param current Loaded bytes
* @param total Total bytes for loading
* @return <b>true</b> - if copying should be continued; <b>false</b> - if copying should be interrupted
*/
boolean onBytesCopied(int current, int total);
}6.5 關閉Dirty文件流
IoUtils.closeSilently(os);6.6 寫入圖片文件
假設沒有出錯,completeEdit裏面,會把dirty文件正式名稱成圖片緩存文件
dirty.renameTo(clean);
然後寫入一條CLEAN或者REMOVE操作日誌到journal文件中。
具體可以看代碼
editor.commit();public void commit() throws IOException {
if (hasErrors) {
completeEdit(this, false);
remove(entry.key); // The previous entry is stale.
} else {
completeEdit(this, true);
}
committed = true;
}private synchronized void completeEdit(Editor editor, boolean success) throws IOException {
...
for (int i = 0; i < valueCount; i++) {
File dirty = entry.getDirtyFile(i);
if (success) {
if (dirty.exists()) {
File clean = entry.getCleanFile(i);
dirty.renameTo(clean); //保存dirty到正式圖片文件
long oldLength = entry.lengths[i];
long newLength = clean.length();
entry.lengths[i] = newLength;
size = size - oldLength + newLength;
fileCount++;
}
} else {
deleteIfExists(dirty);
}
}
redundantOpCount++;
entry.currentEditor = null;
if (entry.readable | success) {// 寫入CLEAN操作日誌
entry.readable = true;
journalWriter.write(CLEAN + ' ' + entry.key + entry.getLengths() + '\n');
if (success) {
entry.sequenceNumber = nextSequenceNumber++;
}
} else {
lruEntries.remove(entry.key); //操作失敗,寫入REMOVE操作日誌
journalWriter.write(REMOVE + ' ' + entry.key + '\n');
}
journalWriter.flush();
if (size > maxSize || fileCount > maxFileCount || journalRebuildRequired()) {
executorService.submit(cleanupCallable);
}
}這樣一次文件保存操作就完成了。
七. BaseDiskCache
BaseDiskCache是抽象類,實現了基本的圖片文件存儲,獲取,刪除等操作,並沒有做什麼限制。
如save和get, remove等操作
public abstract class BaseDiskCache implements DiskCache {
...
protected final FileNameGenerator fileNameGenerator;
...
@Override
public File getDirectory() {
return cacheDir;
}
@Override
public File get(String imageUri) {
return getFile(imageUri);
}
@Override
public boolean save(String imageUri, InputStream imageStream, IoUtils.CopyListener listener) throws IOException {
File imageFile = getFile(imageUri);
File tmpFile = new File(imageFile.getAbsolutePath() + TEMP_IMAGE_POSTFIX);
boolean loaded = false;
try {
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(tmpFile), bufferSize);
try {
loaded = IoUtils.copyStream(imageStream, os, listener, bufferSize);
} finally {
IoUtils.closeSilently(os);
}
} finally {
if (loaded && !tmpFile.renameTo(imageFile)) {
loaded = false;
}
if (!loaded) {
tmpFile.delete();
}
}
return loaded;
}
@Override
public boolean remove(String imageUri) {
return getFile(imageUri).delete();
}
@Override
public void close() {
// Nothing to do
}
@Override
public void clear() {
File[] files = cacheDir.listFiles();
if (files != null) {
for (File f : files) {
f.delete();
}
}
}
protected File getFile(String imageUri) {
String fileName = fileNameGenerator.generate(imageUri);
File dir = cacheDir;
if (!cacheDir.exists() && !cacheDir.mkdirs()) {
if (reserveCacheDir != null && (reserveCacheDir.exists() || reserveCacheDir.mkdirs())) {
dir = reserveCacheDir;
}
}
return new File(dir, fileName);
}
}以save爲例,首先會生成一個tmp文件,然後把網絡圖片文件流寫入tmp文件。
OutputStream os = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(tmpFile),
loaded = IoUtils.copyStream(imageStream, os, listener, bufferSize);然後把tmp文件重新名稱成正式的文件
tmpFile.renameTo(imageFile)八. UnlimitedDiskCache
和BaseDiskCache完全一樣,並沒有新的邏輯
九. LimitedAgeDiskCache
限制存儲時間的文件存儲管理,當我們嘗試獲取緩存文件的時候會去刪除時間過長的文件,存儲的空間沒有限制。
我們以save和get爲例
private final Map<File, Long> loadingDates = Collections.synchronizedMap(new HashMap<File, Long>());@Override
public boolean save(String imageUri, Bitmap bitmap) throws IOException {
boolean saved = super.save(imageUri, bitmap);
rememberUsage(imageUri);
return saved;
}private void rememberUsage(String imageUri) {
File file = getFile(imageUri);
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
file.setLastModified(currentTime);
loadingDates.put(file, currentTime);
}save的時候,會調用rememberUsage方法,使用一個HashMap來存儲緩存時間。
get
@Override
public File get(String imageUri) {
File file = super.get(imageUri);
if (file != null && file.exists()) {
boolean cached;
Long loadingDate = loadingDates.get(file);
if (loadingDate == null) {
cached = false;
loadingDate = file.lastModified();
} else {
cached = true;
}
if (System.currentTimeMillis() - loadingDate > maxFileAge) {
file.delete();
loadingDates.remove(file);
} else if (!cached) {
loadingDates.put(file, loadingDate);
}
}
return file;
}get的時候會根據當前時間和緩存時間比較,如果大於maxFileAge,那麼就刪除它,從而實現了限制時間文件存儲。