大家好, 今天給大家介紹下我們在應用開發中最熟悉而陌生的朋友-----Context類 ,說它熟悉,是應爲我們在開發中
時刻的在與它打交道,例如:Service、BroadcastReceiver、Activity等都會利用到Context的相關方法 ; 說它陌生,完全是
因爲我們真正的不懂Context的原理、類結構關係。一個簡單的問題是,一個應用程序App中存在多少個Context實例對象呢?
一個、兩個? 在此先賣個關子吧。讀了本文,相信您會豁然開朗的 。
Context,中文直譯爲“上下文”,SDK中對其說明如下:
Interface to global information about an application environment. This is an abstract class whose implementation
is provided by the Android system. It allows access to application-specific resources and classes, as well as up-calls
for application-level operations such as launching activities, broadcasting and receiving intents, etc
從上可知一下三點,即:
1、它描述的是一個應用程序環境的信息,即上下文。
2、該類是一個抽象(abstract class)類,Android提供了該抽象類的具體實現類(後面我們會講到是ContextIml類)。
3、通過它我們可以獲取應用程序的資源和類,也包括一些應用級別操作,例如:啓動一個Activity,發送廣播,接受Intent
信息 等。。
於是,我們可以利用該Context對象去構建應用級別操作(application-level operations) 。
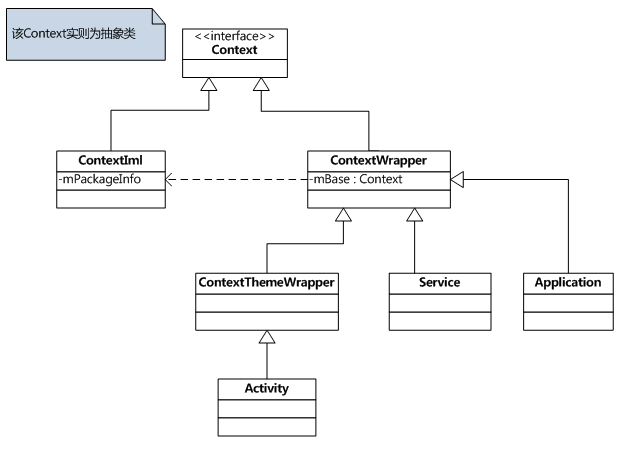
一、Context相關類的繼承關係
相關類介紹:
Context類 路徑: /frameworks/base/core/java/android/content/Context.java
說明: 抽象類,提供了一組通用的API。
源代碼(部分)如下:
publicabstractclass Context {
...
publicabstract Object getSystemService(String name); //獲得系統級服務
publicabstractvoid startActivity(Intent intent); //通過一個Intent啓動Activity
publicabstract ComponentName startService(Intent service); //啓動Service
//根據文件名得到SharedPreferences對象
publicabstract SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name,int mode);
...
}
ContextIml.java類 路徑 :/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ContextImpl.java
說明:該Context類的實現類爲ContextIml,該類實現了Context類的功能。請注意,該函數的大部分功能都是直接調用
其屬性mPackageInfo去完成,這點我們後面會講到。
源代碼(部分)如下:
/**
* Common implementation of Context API, which provides the base
* context object for Activity and other application components.
*/
class ContextImpl extends Context{
//所有Application程序公用一個mPackageInfo對象
/*package*/ ActivityThread.PackageInfo mPackageInfo;
@Override
public Object getSystemService(String name){
...
elseif (ACTIVITY_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
return getActivityManager();
}
elseif (INPUT_METHOD_SERVICE.equals(name)) {
return InputMethodManager.getInstance(this);
}
}
@Override
publicvoid startActivity(Intent intent) {
...
//開始啓動一個Activity
mMainThread.getInstrumentation().execStartActivity(
getOuterContext(), mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), null, null, intent, -1);
}
}
ContextWrapper類 路徑 :\frameworks\base\core\java\android\content\ContextWrapper.java
說明: 正如其名稱一樣,該類只是對Context類的一種包裝,該類的構造函數包含了一個真正的Context引用,即ContextIml
對象。 源代碼(部分)如下:
publicclass ContextWrapper extends Context {
Context mBase; //該屬性指向一個ContextIml實例,一般在創建Application、Service、Activity時賦值
//創建Application、Service、Activity,會調用該方法給mBase屬性賦值
protectedvoid attachBaseContext(Context base) {
if (mBase != null) {
thrownew IllegalStateException("Base context already set");
}
mBase = base;
}
@Override
publicvoid startActivity(Intent intent) {
mBase.startActivity(intent); //調用mBase實例方法
}
}
ContextThemeWrapper類 路徑:/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ContextThemeWrapper.java
說明:該類內部包含了主題(Theme)相關的接口,即android:theme屬性指定的。只有Activity需要主題,Service不需要主題,
所以Service直接繼承於ContextWrapper類。
源代碼(部分)如下:
publicclass ContextThemeWrapper extends ContextWrapper {
//該屬性指向一個ContextIml實例,一般在創建Application、Service、Activity時賦值
private Context mBase;
//mBase賦值方式同樣有一下兩種
public ContextThemeWrapper(Context base, int themeres) {
super(base);
mBase = base;
mThemeResource = themeres;
}
@Override
protectedvoid attachBaseContext(Context newBase) {
super.attachBaseContext(newBase);
mBase = newBase;
}
}
Activity類 、Service類 、Application類本質上都是Context子類, 更多信息大家可以自行參考源代碼進行理解。
二、 什麼時候創建Context實例
熟悉了Context的繼承關係後,我們接下來分析應用程序在什麼情況需要創建Context對象的?應用程序創建Context實例的
情況有如下幾種情況:
1、創建Application 對象時, 而且整個App共一個Application對象
2、創建Service對象時
3、創建Activity對象時
因此應用程序App共有的Context數目公式爲:
總Context實例個數 = Service個數 + Activity個數 + 1(Application對應的Context實例)
具體創建Context的時機
1、創建Application對象的時機
每個應用程序在第一次啓動時,都會首先創建Application對象。如果對應用程序啓動一個Activity(startActivity)流程比較
清楚的話,創建Application的時機在創建handleBindApplication()方法中,該函數位於 ActivityThread.java類中 ,如下:
//創建Application時同時創建的ContextIml實例
privatefinalvoid handleBindApplication(AppBindData data){
...
///創建Application對象
Application app = data.info.makeApplication(data.restrictedBackupMode, null);
...
}
public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass, Instrumentation instrumentation) {
...
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = getClassLoader();
ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl(); //創建一個ContextImpl對象實例
appContext.init(this, null, mActivityThread); //初始化該ContextIml實例的相關屬性
///新建一個Application對象
app = mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.newApplication(
cl, appClass, appContext);
appContext.setOuterContext(app); //將該Application實例傳遞給該ContextImpl實例
}
...
}
2、創建Activity對象的時機
通過startActivity()或startActivityForResult()請求啓動一個Activity時,如果系統檢測需要新建一個Activity對象時,就會
回調handleLaunchActivity()方法,該方法繼而調用performLaunchActivity()方法,去創建一個Activity實例,並且回調
onCreate(),onStart()方法等, 函數都位於 ActivityThread.java類 ,如下:
//創建一個Activity實例時同時創建ContextIml實例
privatefinalvoid handleLaunchActivity(ActivityRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent); //啓動一個Activity
}
privatefinal Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityRecord r, Intent customIntent) {
...
Activity activity = null;
try {
//創建一個Activity對象實例
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = r.packageInfo.getClassLoader();
activity = mInstrumentation.newActivity(cl, component.getClassName(), r.intent);
}
if (activity != null) {
ContextImpl appContext = new ContextImpl(); //創建一個Activity實例
appContext.init(r.packageInfo, r.token, this); //初始化該ContextIml實例的相關屬性
appContext.setOuterContext(activity); //將該Activity信息傳遞給該ContextImpl實例
...
}
...
}
3、創建Service對象的時機
通過startService或者bindService時,如果系統檢測到需要新創建一個Service實例,就會回調handleCreateService()方法,
完成相關數據操作。handleCreateService()函數位於 ActivityThread.java類,如下:
//創建一個Service實例時同時創建ContextIml實例
privatefinalvoid handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data){
...
//創建一個Service實例
Service service = null;
try {
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
}
...
ContextImpl context = new ContextImpl(); //創建一個ContextImpl對象實例
context.init(packageInfo, null, this); //初始化該ContextIml實例的相關屬性
//獲得我們之前創建的Application對象信息
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
//將該Service信息傳遞給該ContextImpl實例
context.setOuterContext(service);
...
}
另外,需要強調一點的是,通過對ContextImp的分析可知,其方法的大多數操作都是直接調用其屬性mPackageInfo(該屬性類
型爲PackageInfo)的相關方法而來。這說明ContextImp是一種輕量級類,而PackageInfo纔是真正重量級的類。而一個App裏的
所有ContextIml實例,都對應同一個packageInfo對象。
最後給大家分析利用Context獲取SharedPreferences類的使用方法,SharedPreferences類想必大家都使用過,其一般獲取方
法就是通過調用getSharedPreferences()方法去根據相關信息獲取SharedPreferences對象。具體流程如下:
1 、調用 getSharedPreferences()獲取對應的的文件,該函數實現功能如下:
//Context類靜態數據集合,以鍵值對保存了所有讀取該xml文件後所形成的數據集合
privatestaticfinal HashMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl> sSharedPrefs =
new HashMap<File, SharedPreferencesImpl>();
@Override
public SharedPreferences getSharedPreferences(String name, int mode){
//其所對應的SharedPreferencesImpl對象 ,該對象已一個HashMap集合保存了我們對該文件序列化結果
SharedPreferencesImpl sp;
File f = getSharedPrefsFile(name); //該包下是否存在對應的文件,不存在就新建一個
synchronized (sSharedPrefs) { //是否已經讀取過該文件,是就直接返回該SharedPreferences對象
sp = sSharedPrefs.get(f);
if (sp != null && !sp.hasFileChanged()) {
//Log.i(TAG, "Returning existing prefs " + name + ": " + sp);
return sp;
}
}
//以下爲序列化該xml文件,同時將數據寫到map集合中
Map map = null;
if (f.exists() && f.canRead()) {
try {
str = new FileInputStream(f);
map = XmlUtils.readMapXml(str);
str.close();
}
...
}
synchronized (sSharedPrefs) {
if (sp != null) {
//Log.i(TAG, "Updating existing prefs " + name + " " + sp + ": " + map);
sp.replace(map); //更新數據集合
} else {
sp = sSharedPrefs.get(f);
if (sp == null) {
//新建一個SharedPreferencesImpl對象,並且設置其相關屬性
sp = new SharedPreferencesImpl(f, mode, map);
sSharedPrefs.put(f, sp);
}
}
return sp;
}
}
2、 SharedPreferences 不過是個接口,它定義了一些操作xml文件的方法,其真正實現類爲SharedPreferencesImpl ,該類是
ContextIml的內部類,該類如下:
//soga,這種形式我們在分析Context ContextIml時接觸過
//SharedPreferences只是一種接口,其真正實現類是SharedPreferencesImpl類
privatestaticfinalclass SharedPreferencesImpl implements SharedPreferences{
private Map mMap; //保存了該文件序列化結果後的操作, 鍵值對形式
//通過key值獲取對應的value值
public String getString(String key, String defValue) {
synchronized (this) {
String v = (String)mMap.get(key);
return v != null ? v : defValue;
}
}
...
//獲得該SharedPreferencesImpl對象對應的Edito類,對數據進行操作
publicfinalclass EditorImpl implements Editor {
privatefinal Map<String, Object> mModified = Maps.newHashMap(); //保存了對鍵值變化的集合
}
}
基本上獲取SharedPreferences 對象就是這麼來的,關於Context裏的更多方法請大家參照源代碼認真學習吧。