DCGAN介紹
原始的GAN網絡在訓練過程中生成者生成圖像質量不太穩定,無法得到高質量的生成者網絡,導致這個問題的主要原因是生成者與判別者使用相同的反向傳播網絡,對生成者網絡的改進就是用卷積神經網絡替代原理的MLP實現穩定生成者網絡,生成高質量的圖像。這個就是Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network (DCGAN)的由來。相比GAN,DCGAN把原來使用MLP的地方都改成了CNN,同時去掉了池化層,改變如下:
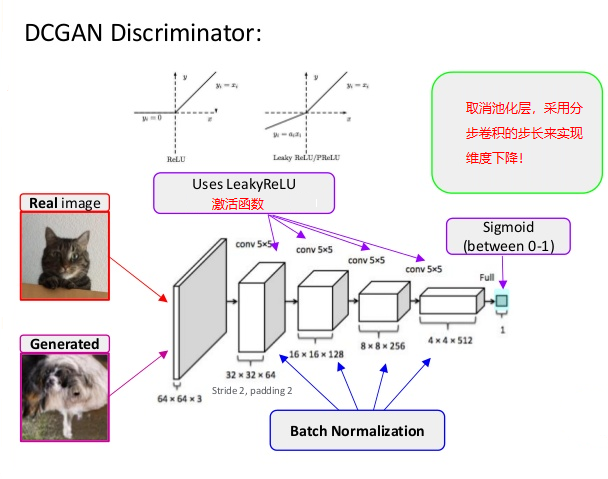
- 判別器使用正常卷積,最後一層使用全連接層做預測判別
- 生成器根據輸入的隨機噪聲,通過卷積神經網絡生成一張圖像
- 無論是生成器還是判別器都在卷積層後面有BN層
- 生成器與判別器分別使用relu與leaky relu作爲激活函數, 除了生成器的最後一層
- 生成器使用轉置/分步卷積、判別器使用正常卷積。
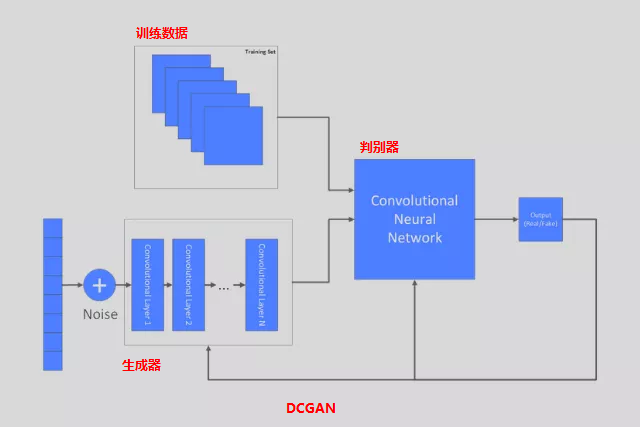
最終DCGAN的網絡模型如下:
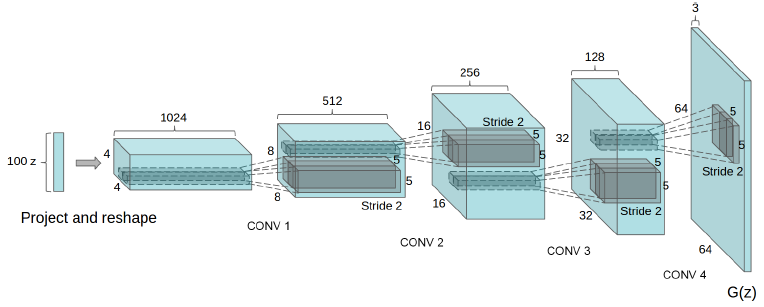
其中基於卷積神經網絡的生成器模型如下:
判別器模型如下:
代碼實現:
生成器:
class Generator:
def __init__(self, depths=[1024, 512, 256, 128], s_size=4):
self.depths = depths + [3]
self.s_size = s_size
self.reuse = False
def __call__(self, inputs, training=False):
inputs = tf.convert_to_tensor(inputs)
with tf.variable_scope('g', reuse=self.reuse):
# reshape from inputs
with tf.variable_scope('reshape'):
outputs = tf.layers.dense(inputs, self.depths[0] * self.s_size * self.s_size)
outputs = tf.reshape(outputs, [-1, self.s_size, self.s_size, self.depths[0]])
outputs = tf.nn.relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
# deconvolution (transpose of convolution) x 4
with tf.variable_scope('deconv1'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(outputs, self.depths[1], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = tf.nn.relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('deconv2'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(outputs, self.depths[2], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = tf.nn.relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('deconv3'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(outputs, self.depths[3], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = tf.nn.relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('deconv4'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d_transpose(outputs, self.depths[4], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
# output images
with tf.variable_scope('tanh'):
outputs = tf.tanh(outputs, name='outputs')
self.reuse = True
self.variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope='g')
return outputs判別器:
class Discriminator:
def __init__(self, depths=[64, 128, 256, 512]):
self.depths = [3] + depths
self.reuse = False
def __call__(self, inputs, training=False, name=''):
def leaky_relu(x, leak=0.2, name=''):
return tf.maximum(x, x * leak, name=name)
outputs = tf.convert_to_tensor(inputs)
with tf.name_scope('d' + name), tf.variable_scope('d', reuse=self.reuse):
# convolution x 4
with tf.variable_scope('conv1'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d(outputs, self.depths[1], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = leaky_relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('conv2'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d(outputs, self.depths[2], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = leaky_relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('conv3'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d(outputs, self.depths[3], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = leaky_relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('conv4'):
outputs = tf.layers.conv2d(outputs, self.depths[4], [5, 5], strides=(2, 2), padding='SAME')
outputs = leaky_relu(tf.layers.batch_normalization(outputs, training=training), name='outputs')
with tf.variable_scope('classify'):
batch_size = outputs.get_shape()[0].value
reshape = tf.reshape(outputs, [batch_size, -1])
outputs = tf.layers.dense(reshape, 2, name='outputs')
self.reuse = True
self.variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope='d')
return outputs損失函數與訓練
def loss(self, traindata):
"""build models, calculate losses.
Args:
traindata: 4-D Tensor of shape `[batch, height, width, channels]`.
Returns:
dict of each models' losses.
"""
generated = self.g(self.z, training=True)
g_outputs = self.d(generated, training=True, name='g')
t_outputs = self.d(traindata, training=True, name='t')
# add each losses to collection
tf.add_to_collection(
'g_losses',
tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=tf.ones([self.batch_size], dtype=tf.int64),
logits=g_outputs)))
tf.add_to_collection(
'd_losses',
tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=tf.ones([self.batch_size], dtype=tf.int64),
logits=t_outputs)))
tf.add_to_collection(
'd_losses',
tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(
labels=tf.zeros([self.batch_size], dtype=tf.int64),
logits=g_outputs)))
return {
self.g: tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('g_losses'), name='total_g_loss'),
self.d: tf.add_n(tf.get_collection('d_losses'), name='total_d_loss'),
}
def train(self, losses, learning_rate=0.0002, beta1=0.5):
"""
Args:
losses dict.
Returns:
train op.
"""
g_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate, beta1=beta1)
d_opt = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=learning_rate, beta1=beta1)
g_opt_op = g_opt.minimize(losses[self.g], var_list=self.g.variables)
d_opt_op = d_opt.minimize(losses[self.d], var_list=self.d.variables)
with tf.control_dependencies([g_opt_op, d_opt_op]):
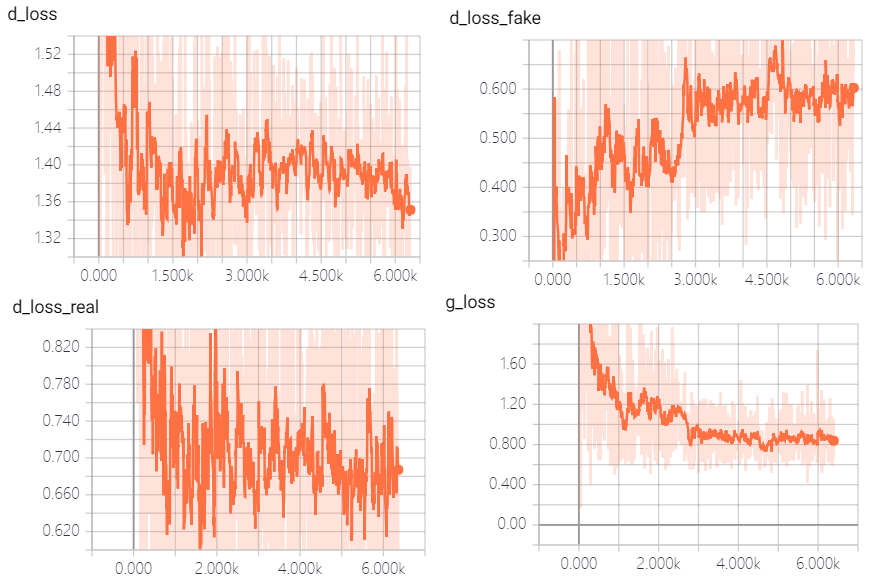
return tf.no_op(name='train')訓練與運行
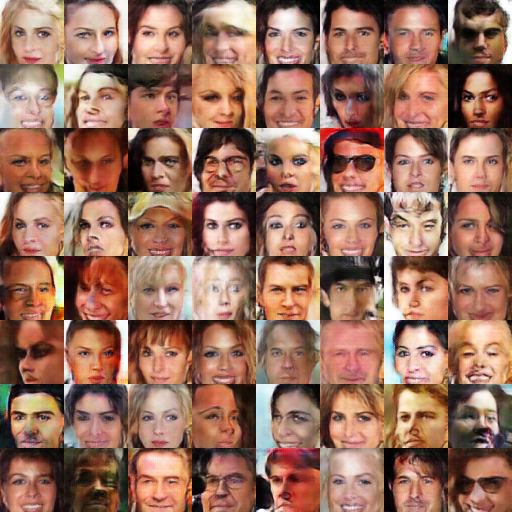
開始
2個epoch之後
5個epoch之後
OpenCV+tensorflow系統化學習路線圖,推薦視頻教程:
計算機視覺從入門到實戰